To simplify the development of cloud-native applications on SAP Cloud Platform, SAP provides two complementary Java-based software development kits (SDKs), which offer a variety of modules that focus on specific development purposes.
Two SDKs
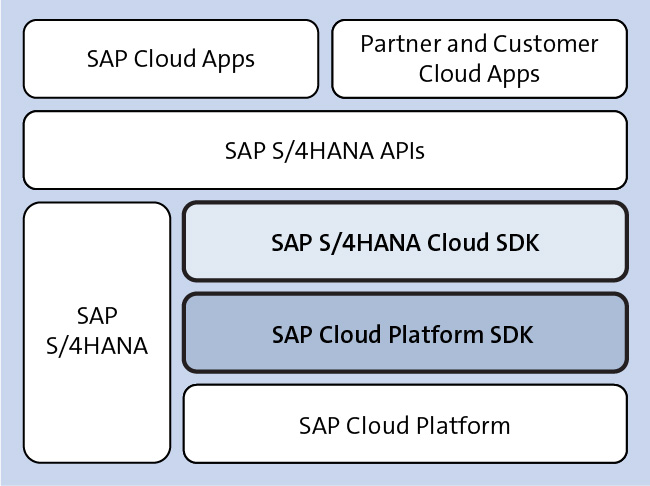
The SAP Cloud Platform SDK for service development provides generic development libraries and tools (for example, OData consumption, OData provisioning, business events) to enable application developers to easily create generic extensions on SAP Cloud Platform.
The SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK is based on the SAP Cloud Platform SDK for service development and provides SAP S/4HANA-specific end-to-end capabilities (such as convenient consumption of data models from SAP S/4HANA), tools, and codified processes (for example, for ensuring quality and interoperability) to enable application developers to easily create SAP S/4HANA side-by-side extensions. The SDK represents the generalized knowledge and experience from building several productively running SAP S/4HANA side-by-side extensions on SAP Cloud Platform. Amongst others, these extensions include partner-built applications as well as SAP RealSpend.
The first figure highlights the relationship of both SDKs with the SAP Cloud Platform and SAP S/4HANA. The SAP Cloud Platform SDK for service development builds upon SAP Cloud Platform whereas the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK builds on top of the SAP Cloud Platform to further simplify the development of side-by-side extensions.
Extension Structure
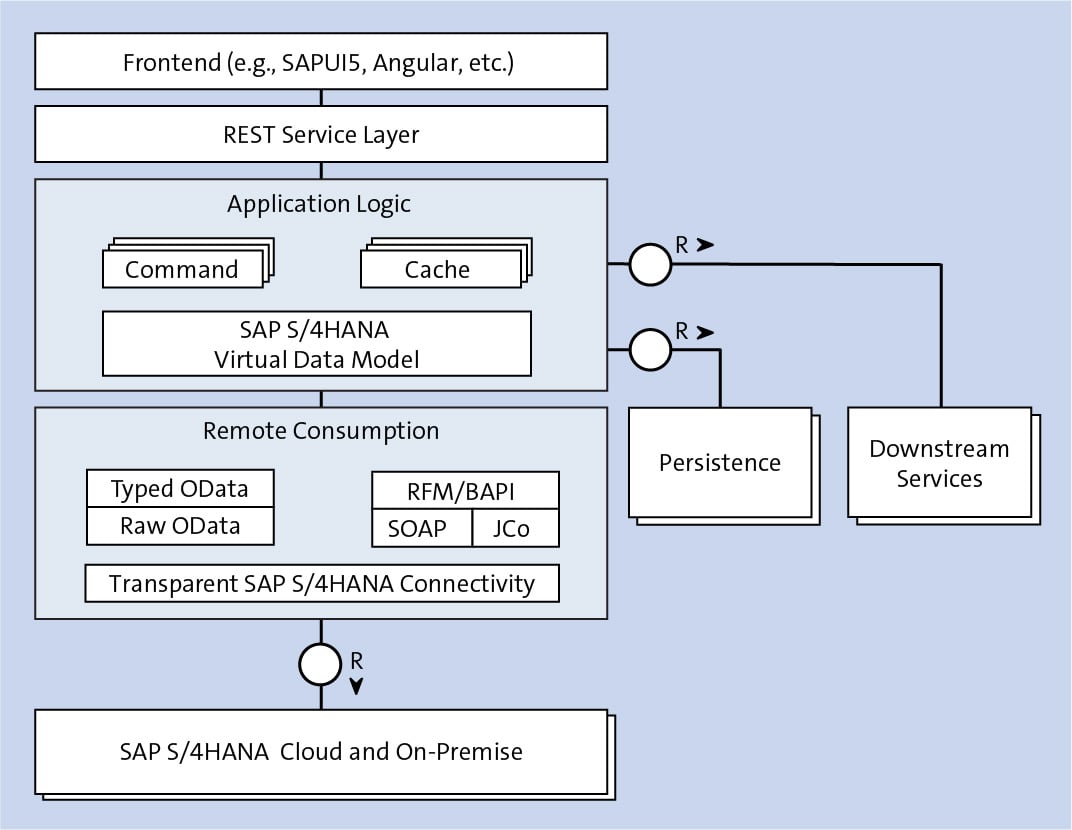
Java-based side-by-side extensions on SAP Cloud Platform tend to follow a certain structure, as shown in the following figure, which depicts the essential components in the stack of side-by-side extensions according to the traditional layers of a three-tiered application.
Frontend Layer
The consumer-facing part of a side-by-side extension is usually the frontend of the application. This layer is usually built in JavaScript or TypeScript using frontend technologies such as SAP Fiori, SAPUI5, Angular, and more.
REST Service Layer
Below the frontend layer, the REST service layer exposes the functionality of a side-by-side extension using RESTful APIs. This layer may consist of simple JSON-based APIs or more sophisticated APIs built on the OData standard. The service layer can be exposed with Java-based frameworks such as Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE), Spring, or plain web servlets. In addition, the SAP Cloud Platform SDK for service development offers functionality for exposing OData services in an easy and convenient way.
Application Logic Layer
The Java-based application logic is at the heart of a side-by-side extension. This layer primarily consists of classes that realize the functionality of the application (such as persistence). For this layer, to efficiently build extensions for SAP S/4HANA, the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK offers a virtual data model (VDM), which is a Java-based representation of the logic required to consume services that are offered by SAP S/4HANA. The VDM allows you to invoke the relevant APIs of SAP S/4HANA—consisting of both OData services and specific BAPIs—in a type-safe and convenient way from within the Java code.
In addition, to retrieve information via other systems or microservices in a resilient and fault-tolerant manner, the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK offers commands. Commands represent function-oriented wrappers around specific parts of the code that interact with other components or services that may be unavailable or prone to latency issues.
Closely related to the concept of commands are caches that can store results that were previously been retrieved via remote services. This functionality allows us to improve the responsiveness of the application and reduce the load on downstream services or systems such as SAP S/4HANA.
Remote Consumption Layer
Finally, the remote consumption layer represents the foundation for integration capabilities such as the SAP S/4HANA VDM by realizing a transparent connectivity layer to SAP S/4HANA systems. This layer includes abstractions that allow the consumption of both OData services and BAPIs via different underlying protocols—SOAP and the RFC protocol, which is implemented based on the SAP Java Connector (JCo).
In particular, these abstractions facilitate the development of cost-efficient multitenant applications where customers (or their administrators) can configure connections to their relevant SAP S/4HANA systems. For developers of a side-by-side extension, whether data is retrieved from an SAP S/4HANA system in the cloud or from a system that resides in an on-premise environment remains fully transparent, and the data is exposed to a side-by-side extension with the Cloud Connector.
Additional Tools
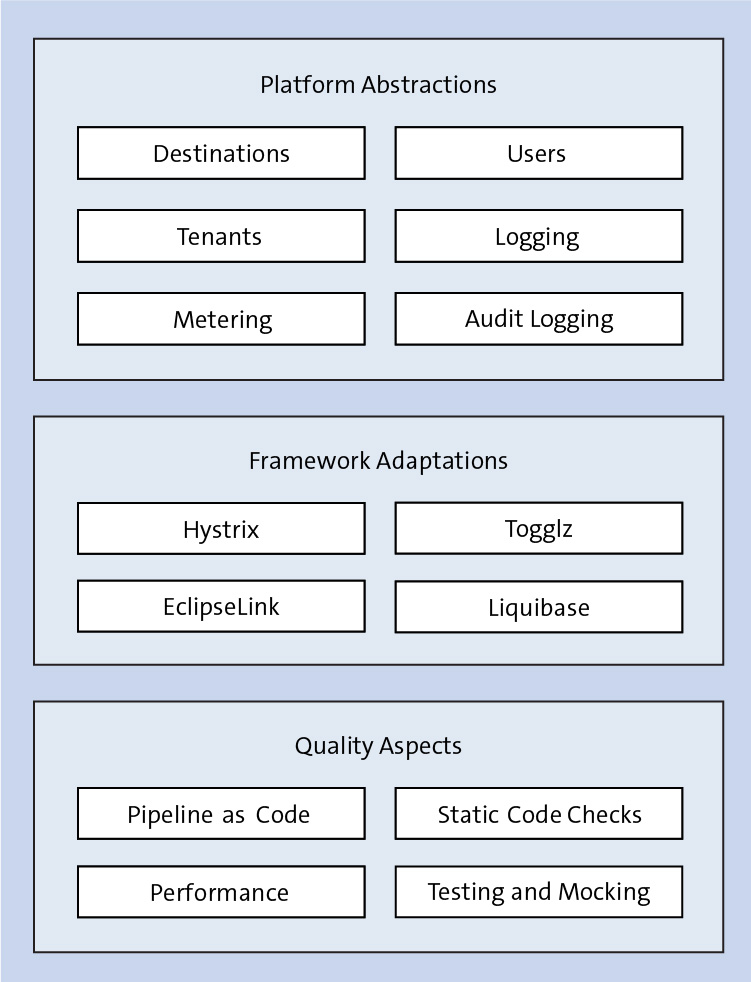
In addition to the application layer-specific functionality offered by the SAP Cloud Platform SDK for service development and the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK, a wide variety of tools and components are available to address additional aspects across the layers we’ve just described. These tools also refer to capabilities focusing on both the development and the operation of a side-by-side extension. The final figure below shows an overview of these components.
Platform Abstractions
The SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK supports both SAP Cloud Platform environments: Cloud Foundry and Neo. Therefore, it abstracts from the specific implementations of each underlying environments. It offers generic interfaces for environment-specific tasks such as accessing destinations, as well as tenant and user data. This facilitates testing across SAP Cloud Platform environments and offers increased flexibility for running the same code on Cloud Foundry and Neo.
Framework Adaptations
Open source libraries offer powerful capabilities for developing SAP S/4HANA side-by-side extensions. Nevertheless, open source components sometimes rely on assumptions that do not fully fulfill the requirements of enterprise applications. Therefore, the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK offers specific adaptations and extensions to certain open source frameworks to consider these requirements. An example of an adaptation is the extension Togglz, which supports feature toggling on both the user level and the tenant level.
Quality Aspects
Delivering a cloud-native side-by-side extension not only requires developing code efficiently but also continuously ensuring high standards. Therefore, the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK offers a variety of tools for testing as well as a ready-made, codified, and fully containerized pipeline that enables continuous testing and delivery of side-by-side extensions.
Conclusion
When it comes to developing cloud-native applications on SAP Cloud Platform, you have quite a few options. This blog post provided a high-level overview of your options. Which option do you think would work best for your project?
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book Extending SAP S/4HANA: Side-by-Side Extensions with the SAP S/4HANA Cloud SDK by Philipp Herzig, Henning Heitkötter, Sander Wozniak, Akhil Agarwal, and Johannes Wust.




Comments