Even though Earth is zipping through space at 67,000 mph, it can often seem like the business world is moving even faster.
Just look back at the past decade. Who would have envisioned the adoption of new and exciting technology such as augmented reality and self-driving cars back in 2010? Even SAP HANA was still in development when the decade began.
And those are just the things that everybody seems to know about; there is plenty more to learn. Consider this: according to SAP, 40% of organizations pursuing digital transformation are utilizing robotic process automation (RPA) services in their initiatives, and by 2022 Forbes estimates the RPA software market will total $3.7 billion.
If you don’t know what RPA is, or just found out about it recently, you’re not alone. I had no clue what this technology was until last summer when we signed an E-Bite on the topic—even though the idea behind it, I’d come to find, had been prevalent in my own everyday life for years.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
So what is RPA? Simply put, RPA is a way for organizations to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks such as processing purchase orders or collecting information from an Excel spreadsheet and moving it somewhere else. In a more relatable context, consider the emails you get from a company soon after adding some items to a cart but not yet purchasing them. The series of emails you receive, sometimes with a coupon enticing you to complete your purchase, is an example of RPA technology at work. Humans aren’t sending out hundreds of abandoned cart emails every day; rather, a set of pre-defined logic is running and sending you content.
RPA logic is fed to programmable bots that operate in one of two ways. In the first, a bot can perform a task when prompted by a human user. These types of RPA bots are called “attended” bots due to this dependency. Once the task has been initiated, however, the bot takes over and does what it’s been programmed to do. It may sometimes ask the human for additional input, but more or less, the task is automated.
Alternatively, an “unattended” bot is one that is trained to work autonomously and without input from a human. Think of the shopping cart email above. The bot knows to send those who abandoned their shopping cart a set of emails, and knows when to stop sending the emails based on whether the customer completes their purchase or not.
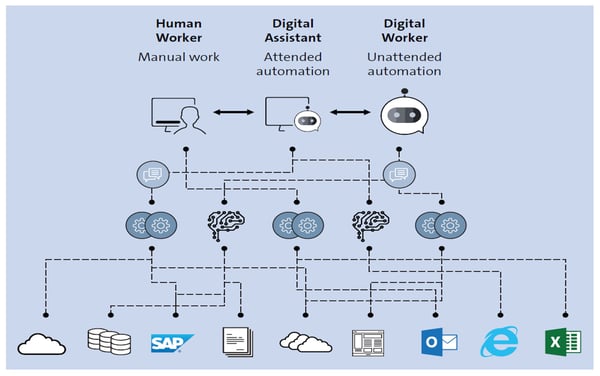
The incentive to using RPA is greater efficiency. Streamlining processes such as supply chain, data, and sales order management saves money, and the humans that used to perform those activities are now freed up to do other, more important tasks such as analyzing the results of campaigns and making smarter decisions with that data.
SAP Intelligent RPA
SAP takes the idea of RPA even farther by utilizing machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) technology. Rather than being provided a set of written logic to follow, bots “watch” users perform processes, intuit the logic behind them, and determine how to do the same tasks themselves.
It would make sense, then, that SAP has named this SAP Intelligent RPA—after all, machine learning and AI are two intelligent technologies at the forefront of today’s lightning-fast business landscape.
But while the data intelligence industry is growing at a rapid pace, others are stagnant and risk becoming obsolete without major change themselves. One such industry is oil and gas, responsible for two trillion dollars of the global economy but currently at a crossroads when it comes to its future.
Challenges Facing the Oil & Gas Industry

Oil and gas companies have been around since the mid-19th century and have played a large part in world events as the main sources of energy harvesting and production. As the years have passed, the industry has found itself at risk from a handful of factors: volatility of the market, regional conflict, reliability of existing drilling and refining sites, and climate change and the related push for alternative energy sources.
Not all of these issues are solvable by RPA, however—not even all can be solved by intelligent technologies. But when it comes to obtaining greater efficiency and cost savings at scale, RPA can help.
SAP Intelligent RPA for the Oil & Gas Industry
SAP Intelligent RPA currently has 40+ content packages, with more than half that could be utilized in the oil and gas industry. Here’s a list of just some of them:
- Activate Communication Arrangement
- Automated Upload of General Ledger Entries
- Automatic PGI for Outbound Deliveries with NON-Warehouse
- Automated Upload of Supplier Invoices
- Business Partner Master Data Check
- Create Just-in-Time Calls
- Create Product Master Data with Reference (cloud and on-premise)
- Create Sales Inquiry
- Inconsistent New-GL Open Item Exclusion for Migration Cockpit
- Intelligent Production Order Conversion
- Maintain Planned Independent Requirements
- Manage Payment Advice
- Mass Printing of Production Order Picklist
- Post Goods Movement
- Process Order Confirmation
- Production Order Completion
- Production Order Operation Confirmation
- Simple Purchase Requisition Creation from Excel
- Smart Accruals Collector
- Supplier Invoice Status Checks (cloud and on-premise)
With these in mind, here are three ways that SAP Intelligent RPA can transform the oil and gas industry.
Efficient Production
With constant product demand, it’s important that oil and gas firms produce enough to meet it. This can be tricky; while seasonal demand fluctuations can be factored into production schedules, unforeseen events such as natural disasters and pandemics can increase or decrease demand overnight.
By being proactive and automating certain processes ahead of time, firms can avoid bottlenecks when understaffed or overworked. RPA can automate time-consuming processes such as mass-printing of picklists, posting goods movement, and creating product master data for semi-finished or finished products.

Many PO-related tasks can also be automated. Further, SAP Intelligent RPA can help avoid downstream delays by proactively checking for missing master data and alerting users, creating communication arrangements based on a predefined scenarios list, automating data processing, and generating planned independent requirements given production data and timeframes with SAP Intelligent RPA. For example, make-to-stock POs listed in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet can be automatically confirmed, planned orders can be turned into POs, PO operation confirmation can be given automatically upon production start, and completed POs can be changed via API to the Technically Complete status.
Streamlined Lead-to-Cash
Production is only half the battle for oil and gas firms. With fluctuating prices and constant competition, it’s important for them to lock in prices and collect payment in a timely manner.
A number of SAP Intelligent RPA content packages can be utilized to streamline this lead-to-cash process. As mentioned in the section above, bots checking for missing master data can help avoid snags down the line, one of which includes the lack of information needed to complete the deal.
Financial-related content packages help automate certain processes that can take up employees time, such as invoice status checks—with the option to alert non-paying customers that their payments are due. Mass-printing of PO picklists also takes a lot of time; with an RPA bot, employees are freed up to work on other tasks.
Other automation possibilities include uploading emailed invoices to SAP S/4HANA Cloud, sending emailed journal entries to an SAP Fiori application for posting, creating purchase requisitions from an Excel spreadsheet, enabling smart accruals from spreadsheet to accounting system, creating sales inquiries via screen scraping, and collecting information on inconsistent documents and removing them from SAP S/4HANA.
Cost Reduction
Both the increased efficiency and streamlined lead-to-cash process results in cost reductions as employees are free to perform other tasks. Beyond the SAP Intelligent RPA bots already described, there can be further cost reduction with other bots. For example, automated invoice clearing can be enabled with the Manage Payment Advice package.
Conclusion
There are applications for process automation in the oil and gas industry, and firms would be remiss if they didn’t explore them. Utilizing SAP Intelligent RPA bots is one simple way to increase efficiency and reduce costs. Other considerations might include adding smart technology such as sensors to pipelines; with the IoT data that comes back, potential maintenance issues will be easier to predict, avoiding costly shutdowns.
Want to learn more about SAP Intelligent RPA? We’ve published an E-Bite introduction to the technology. Dive deeper into the automation process and see how to manage and execute projects utilizing SAP Intelligent RPA. If this blog post piqued your interest and you’re looking to join the 40% of your peers already using RPA technology, take a look at Introducing SAP Intelligent Robotic Process Automation.

Comments