SAP S/4HANA Sales covers a wide variety of sales processes, offering very flexible business configuration for integration with procurement, logistics, and finance.
When companies sell physical products, there are different possibilities: products are either sold from stock or, if products are not available, they can be produced, procured, or organized from another warehouse (stock transfer).
The sales process within SAP S/4HANA can start with a sales inquiry, followed by a quotation, which then can be used as a reference to create a sales order (see the figure below). Sales orders can also be created based on long-term agreements such as sales contracts or scheduling agreements. Sales contracts are outline agreements to provide products in certain quantities or for a certain value within a certain time. Scheduling agreements agree on delivering a product in a certain quantity at regular intervals. Sales order processing includes the calculation of prices by the pricing component and checking the availability of ordered products using the available-to-promise (ATP) check.
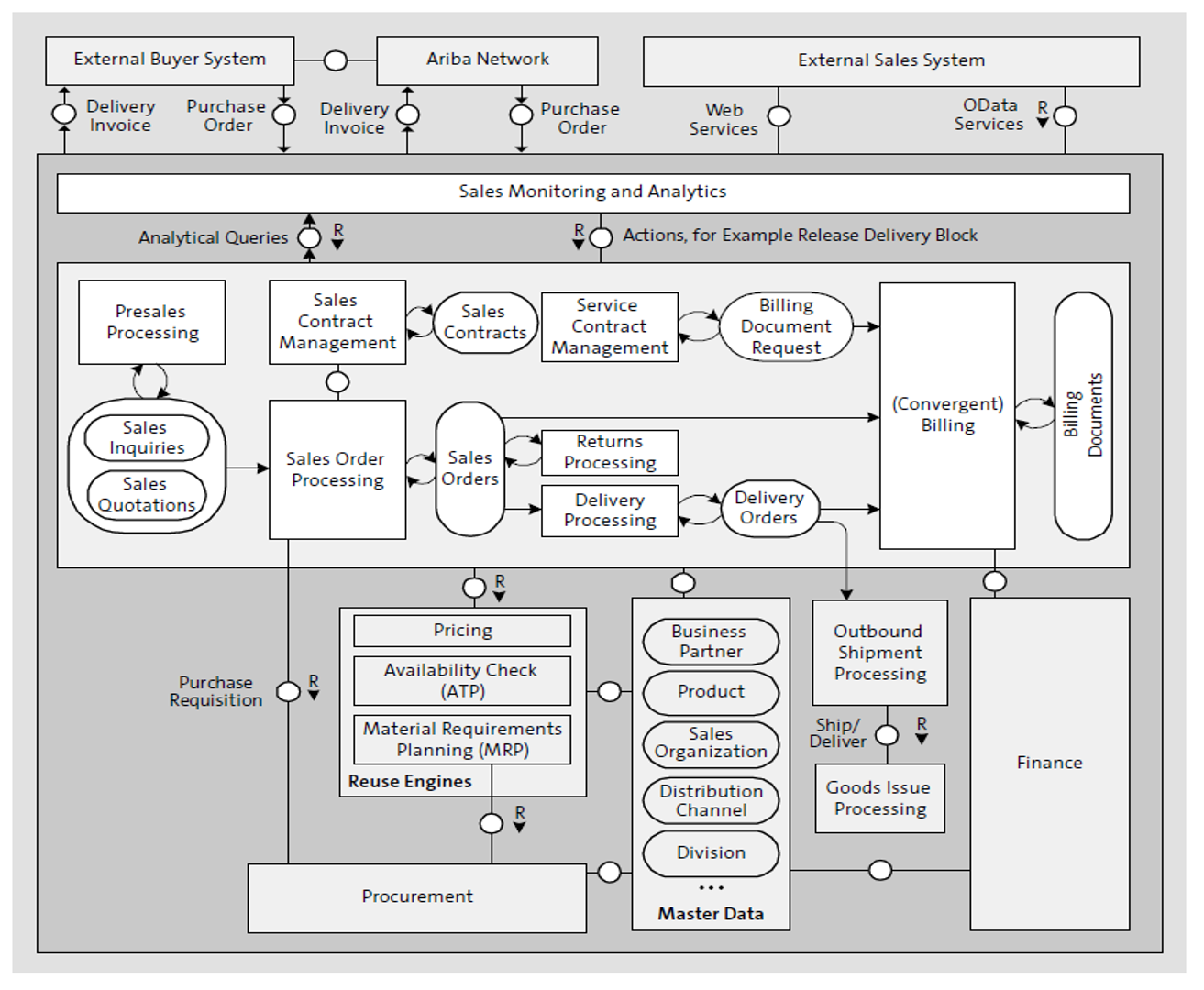
When a sales order includes products that aren’t available in stock, this can lead to in-house production or procurement from third-party vendors. Sales order requests are used to control the conversion of the raw data into a sales order when a sales order will be created from unstructured data.
Master data, such as business partner and product master data, and organizational units such as sales organization, distribution channels, and divisions, play important roles during sales processing.
Outbound deliveries are created to get the products shipped to the customer as promised in the sales order.
Billing usually represents the final step within the sales process. It creates billing documents, which are sent to customers to invoice them for products or services that have been sold. In addition to billing of sales order-related deliveries, there are also other billing scenarios, including omnichannel convergent billing or the creation of preliminary billing documents. Finally, billing documents are posted to financial accounting, resulting in the creation of corresponding Universal Journal entries.
Sales monitoring and analytics features are available across the core sales business processes. Analytical CDS views reading directly from the SAP HANA database tables allow real-time aggregation and calculation of key performance indicators for sales managers. Machine learning regression algorithms allow predictions of future sales potential or processing delays.
Learn SD with SAP S/4HANA in Our Rheinwerk Course!
Dig into SD! Understand the organizational structure and master data in SAP S/4HANA. Learn to customize basic and cross-functional settings in SAP S/4HANA, and then focus on SD processes and their configuration: ATP, pricing, sales processing, shipping, and billing. Take a close look at SD simplifications and enhancements to get the most out of your system! Get access to course recordings by clicking the banner below.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book SAP S/4HANA Architecture by Thomas Saueressig, Tobias Stein, Jochen Boeder, and Wolfram Kleis.


.jpg?height=600&name=SAP%20Fiori%20Apps%20for%20SAP%20S4HANA%20SD%20(2).jpg)

Comments