SAP Master Data Governance (SAP MDG) enables businesses to consolidate and govern master data.
Master data is shared across an enterprise to run business operations, add meaning to transactions, and help manage the unstructured data and associated enterprise metadata. The identification of master data varies from industry to industry and across business process definitions. Master data can also be reference data with less frequent definition changes.
SAP MDG supports key master data objects, such as material master, business partner, customer master, supplier master, contract accounts receivable and payable (FI-CA), internal orders, and finance master data objects such as general ledger accounts, cost center, profit center, and so on. SAP MDG provides reusable templates and frameworks to extend the standard functionality and to govern custom master data objects. SAP also supports partner-developed solution extensions for master data objects related to enterprise asset management, and to retail article master.
SAP MDG has other data management capabilities as well, such as hierarchy processing, mass processing, data integration, data quality evaluation, data quality management, and process analytics.
The main SAP MDG use cases are as follows.
Central Governance
Create and maintain master data in a central system adhering to the data rules and standards. The maintained master data is then replicated to satellite systems, which use the quality master data for the downstream system transactions, as illustrated in this figure.
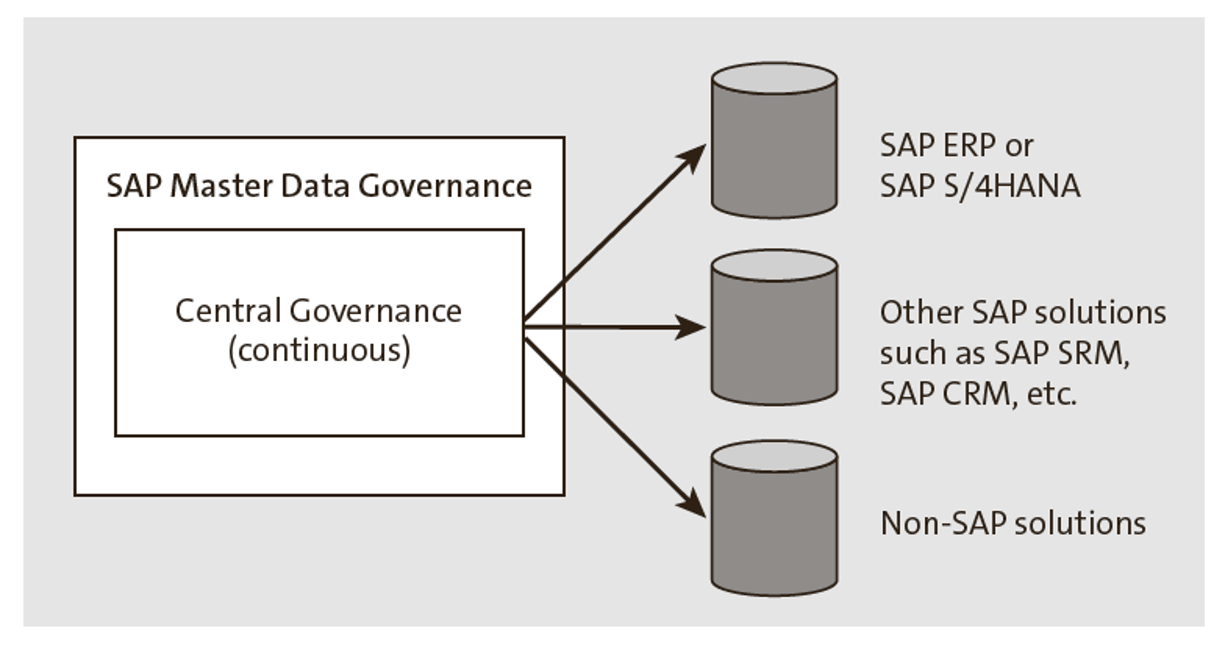
Up-front governance of master data through a clear and transparent audit trail provides significant business benefits from both process- and business operations perspectives. This eliminates error-prone manual master data maintenance processes in multiple satellite systems. Centralized governance and replication of data to target systems delivers consistent data definition and mapping for master data entities across systems and ensures harmonized master data across enterprises by leveraging the key mapping functionality with SAP MDG.
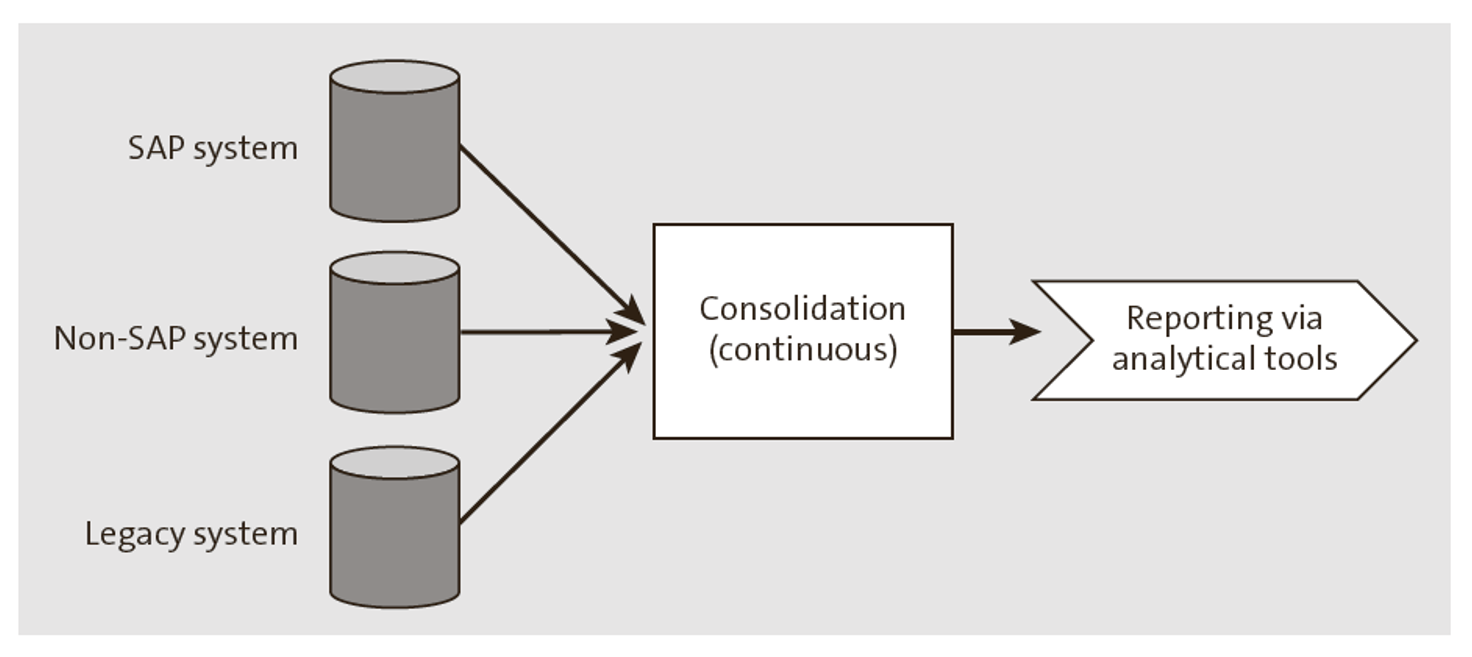
Consolidation for Analytics Purpose Only
Master data is created in separate systems/transactional systems, as needed. The data is then consolidated into a central system by merging and mapping the data to a common data standard, so it can be used for analytics purposes, as illustrated below.
Consolidation for Initial Load Before Central Governance
The consolidation functionalities of merging and best record creation can be used for existing data preparation activities for the central governance scenario. This can be a one-time activity where an enterprise decides to centrally govern the master data and then replicate the data to multiple systems. As part of the initial load, data is extracted, cleansed, and then consolidated using the consolidation scenario.
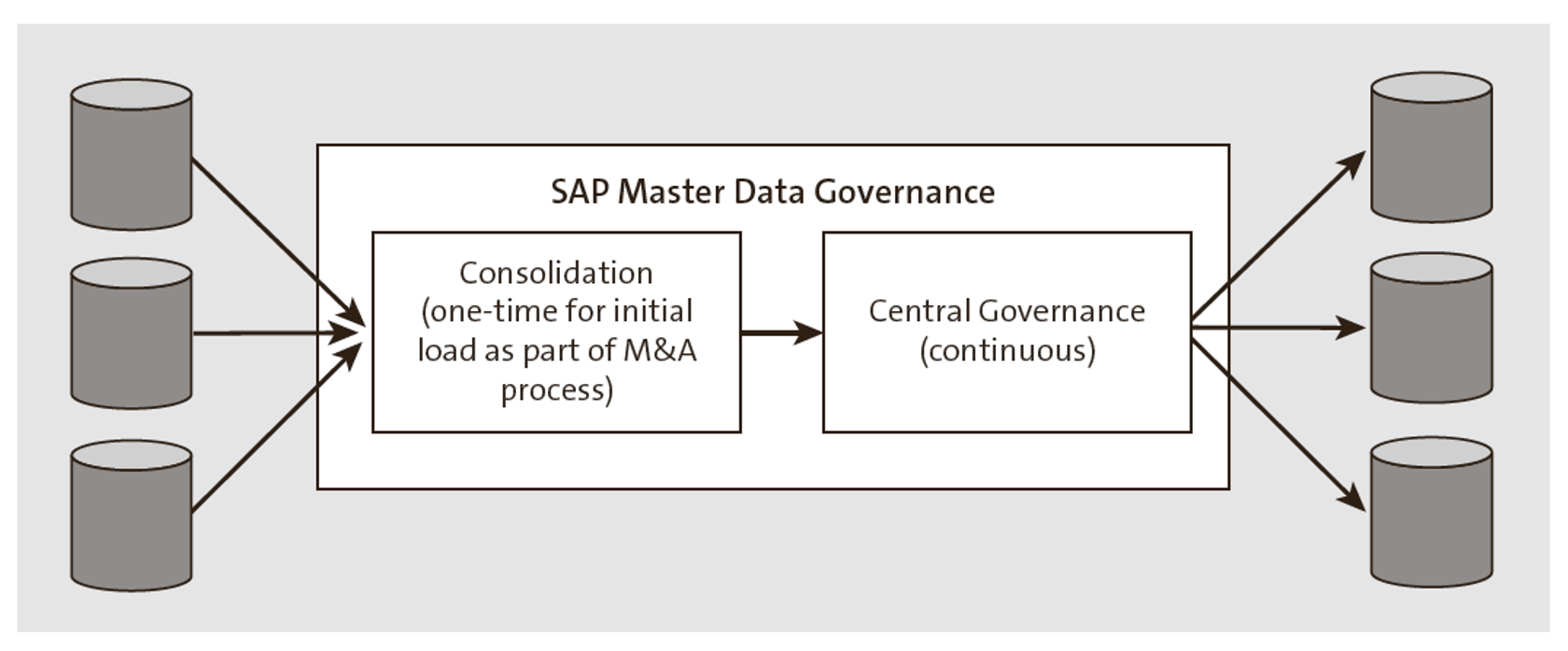
Consolidation for Mergers or Acquisitions
When new systems are introduced into the landscape, consolidation can be used to harmonize and de-duplicate the new data with the existing data.
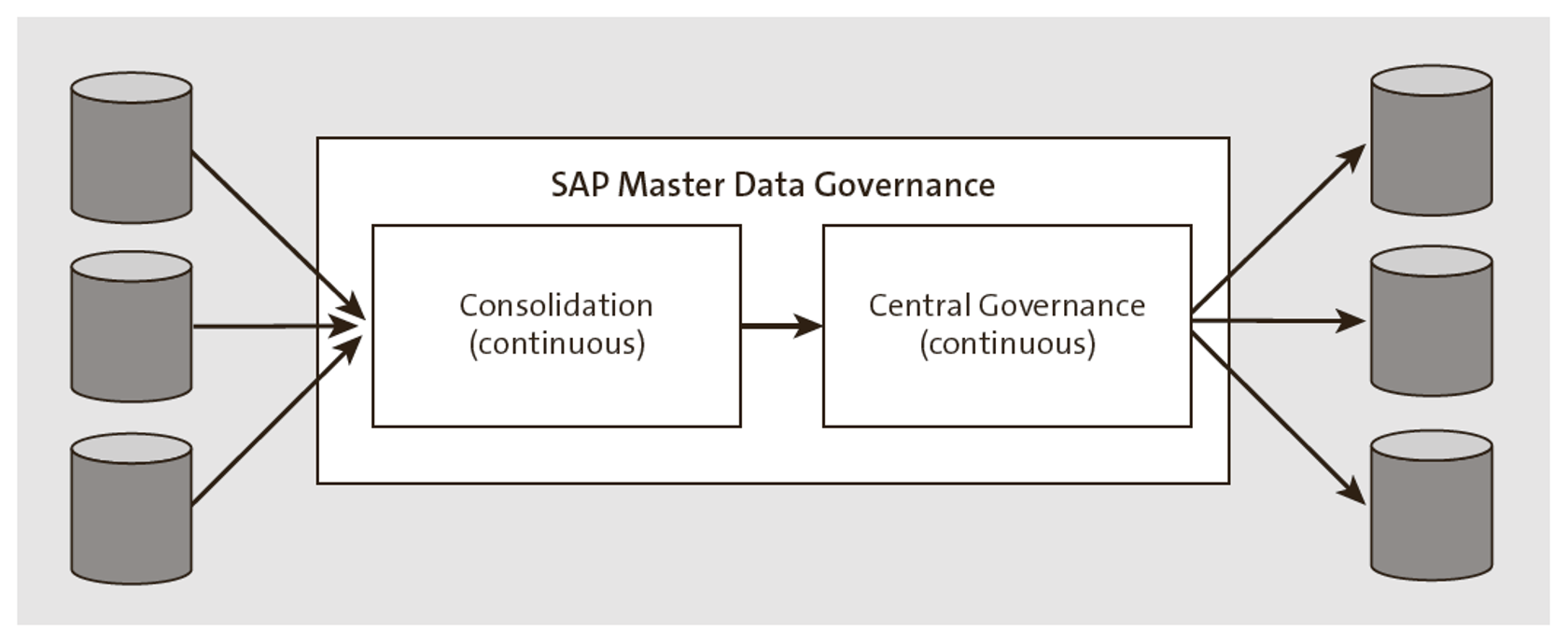
Continuous Hybrid Approach
Both consolidation and central governance scenarios can be implemented together to refine master data from the source systems and govern the enhanced data through the central governance process, as illustrated in the final figure.
To support these use cases, SAP Master Data Governance provides the following functionalities:
- Flexible business-driven/oriented workflow and workflow rules framework are provided to automate master data management processes.
- Tight integration with the SAP data model for key master data domains helps to reduce the total cost of implementation by reusing the data validation and mapping logic. This also helps provide contextual information on the master data record with the linked transactions.
- Frameworks are provided to configure custom master data objects for data management and extension capabilities for standard master data objects.
- Application programming interfaces (APIs) and integration capabilities are provided to enrich the data and provide change logs.
- Built-in master data stewardship tools are provided to monitor data management processes.
- The business rules repository is used to manage data quality rules and analyze data quality for product and business partner master records. Correction of these data quality issues (data quality evaluation) occurs via worklists and embedded analytics.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the SAP Master Data Governance: The Comprehensive Guide by Bikram Dogra, Antony Isacc, Homiar Kalwachwala, Dilip Radhakrishnan, Syama Srinivasan, Sandeep Chahal, Santhosh Cheekoti, Rajani Khambhampati, Vikas Lodha, and David Quirk.



Comments