All persons and organizations involved in business processes in SAP CRM are mapped as business partners.
Because business partners can appear in different roles (e.g., as an organization, ordering party, contact person, or employee), these exact roles are also mapped as business partner roles in SAP CRM. The business partner role thus defines which rights and obligations a business partner has in a business transaction in the SAP system.
Master Data of Business Partners
Business partners are stored in different business partner types, which specify whether the business partner is mapped as a person, organization, or group in the SAP system. Business partners can generally occur as follows:
- Account: An account corresponds to a company, person, or group with whom you have a business relationship. Accounts include, for example, vendors, prospects, ordering parties, ship-to parties, consumers, or sales partners as channel partners.
- Contact person: Contact persons are people in companies with whom you maintain business relationships. The contact person is usually assigned to the company via a business partner relationship.
- Employees: The business partner in the business partner role of the employee corresponds to the employee in your company who fosters or initiates business relationships with customers, vendors, or ordering parties. However, in the case of a shared service center, the employee can also be treated as processor and requester.
These business partner roles, which are available in SAP CRM as in SAP ERP, can be enhanced either as an individual industry solution or with customer-specific requirements. Business partners in SAP CRM include further information in addition to the business partner role.
Business partner relationships define the type of relationship between two business partners. Relationships may be assigned properties, such as a company address. The following figure shows different types of business partners and the possible relationships between them.
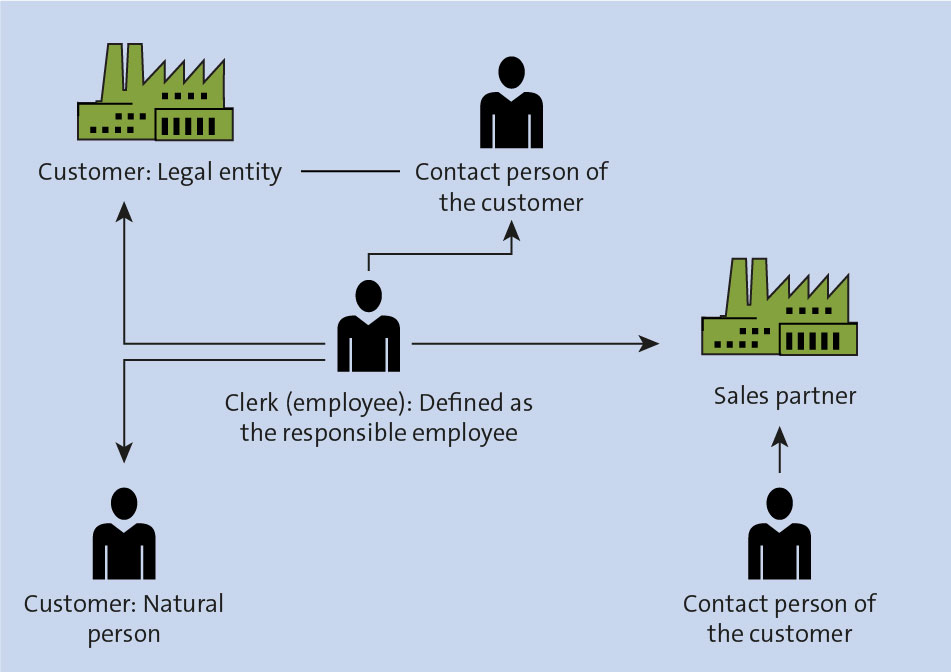
This means, for example, that an employee in the company is maintained as the employee responsible for a particular customer. As a result of this relationship, the employee responsible is also maintained in all business transactions related to the customer.
Business partners in SAP CRM can also be assigned classification or marketing attributes. These are freely definable criteria for categorizing a business partner. The categorization can be used for segmentation or, in certain marketing activities, for target group definition of business partners in marketing.
You can maintain addresses for different address types for each business partner. For example, you can distinguish between the invoicing address and the delivery address. You can also maintain general data for each business partner, such as the types of communication you may use to contact the business partner.
To determine whether a business partner is no longer valid for business Archiving transactions, you can flag it for archiving. This business partner can subsequently be archived and deleted from the database.
You can maintain sales area data for a business partner to determine the sales area for which its business transactions are to be created. These include information on the sales organization, division, and distribution channel.
Another functionality for the business partner is the information sheet. All information on the business partner is displayed in a summarized form on the information sheet. This may be general information on the business partner, business transactions, or information from connected systems. The business partner can download the information sheet in a PDF so that it can also be made available offline.
All changes that affect the business partner are logged in change history. To restrict access to business partners using authorizations, you can create authorization groups in Customizing and subsequently assign them to the business partner.
Transactional Data of Business Partners
Transactional data maps business transactions in SAP CRM. These refer to certain master data, such as customers, prospects, and products. In SAP CRM, transactional data may be, for example, activities, customer and service orders, leads, sales opportunities, or invoicing documents. This data can be clearly assigned to a customer. We’ll now show you the typical information that is stored in the respective business transactions.
Transactional data contains, for example, information about a product that is the subject of the business transaction, including product details and the price of the product. This information is relevant for carrying out the subsequent processes in SAP ERP, such as invoicing or shipping the product.
Furthermore, all parties involved—the customer, the contact person at the customer, the employee responsible for the process, and possibly other employees working on the process—are assigned to the respective business transaction.
A document can be assigned to a sales organization and contain additional information in the form of notes or attachments.
Data Exchange with Other SAP Systems
Data can be exchanged with different backend systems in a variety of business areas in SAP CRM. Typical cases are the exchange with SAP ERP and SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW).
Business partner data and documents are usually replicated in SAP ERP as SAP ERP soon as a potential customer (prospective customer) has become a customer with an associated sales offer and customer order. SAP ERP is usually the preferred system for customer data because payment processing also takes place there. The maintenance authority for the customer is then also in SAP ERP. When business partner data is replicated, business partner fields, such as Business Partner Role, Name, Address Details, and Business Partner Relationship, are also transferred.
The data from SAP CRM can also be transferred to SAP BW. In SAP BW, reports can be created using SAP CRM data to check, for example, which products are sold the most or what the anticipated sales pipeline for the next quarter looks like.
The planning tool Business Planning and Simulation (BPS) can be used to execute planning with such data. BPS is part of SAP BW and can be fully integrated with SAP CRM. It will be prompted automatically on the user interface of the SAP CRM Web Client when you start key figure planning in SAP CRM, although it does run in a different system.
Report Options for Business Partners in Marketing
To conduct personalized marketing activities for business partners, as much information as possible must be collected from customers.
Business partners can be filtered according to certain criteria and divided into target groups. These criteria are, for example, the age of the customer, occupation, income, and hobbies. They are defined using marketing attributes that can be freely defined by the marketing manager.
These marketing attributes and their values are then ready to be assigned to the business partner. Marketing attributes are structured so that all attributes are collected in one attribute group. This attribute group contains various attributes to which values are then assigned in the business partner. This group can now be assigned various attributes, such as Hobby, Salary group, and so on. The values can also be determined in advance.
The user then selects, directly from the customer, the marketing attribute Hobby and can also add default values from a list. These values can be used to create target groups for customer-specific marketing activities. This marketing activity is, for example, the sending of product recommendations to special customer groups that have been identified via the target groups.
Conclusion
Navigating “business partners” in SAP is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to securing your information. We hope this blog helps you continue your learning when it comes to data privacy.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book GDPR and SAP: Data Privacy with SAP Business Suite and SAP S/4HANA by Volker Lehnert, Iwona Luther, Björn Christoph, Carsten Pluder, and Nicole Fernandes.




Comments