There are some errors that can occur during the replication process in SAP systems that may require manual intervention.
In this post, let’s discuss these errors and how to respond to them effectively to minimize the impact on real-time replications in the following sections.
Duplicate Key Issue
If the initial load of data is interrupted due to a planned or unplanned outage, once the systems involved in replication process are back up and running, SAP LT Replication Server tries reconnecting automatically to the source and target systems and resuming the load process. When that happens, the user may encounter an error: Cannot insert record in target system (duplicate key error).
This is very much the system behaving as designed. This is because the portion of data was inserted in the target system, but SAP LT Replication Server is not yet aware that the data load was successful before the system failure. Consequently, when the system is back up, SAP LT Replication Server reattempts loading the very same data, leading to the duplicate key error message. You can resolve this by changing the write behavior to Array Modify, as shown in the figure below. To change the write behavior, log into SAP LT Replication Server and enter Transaction LTRC. Select the MTID and navigate to the Data Transfer Monitor tab, select the table, and click the Edit button, which can be found in the left middle (pencil icon). Change Write Behavior to 3 (Array Modify).

Cannot Replicate Data from Table XXX, Different Trigger Option Exists
This error is usually seen when the user tries replicating a table from the same source system to different target systems. In general, for an application table (e.g., table SFLIGHT), SAP LT Replication Server shares the same logging table and triggers when replicating it to different targets.
The main cause of the Cannot Replicate Data from Table XXX, Different Trigger Option Exists error usually is a difference in the configuration settings. Check if the Allow Multiple Usage and Read from Single Client settings in the SAP LT Replication Server configuration are consistent across all configurations when planning to replicate a table to different targets. To do so, go to Transaction LTRC, enter the MTID, and navigate to the Administration Data tab, as shown in this figure.
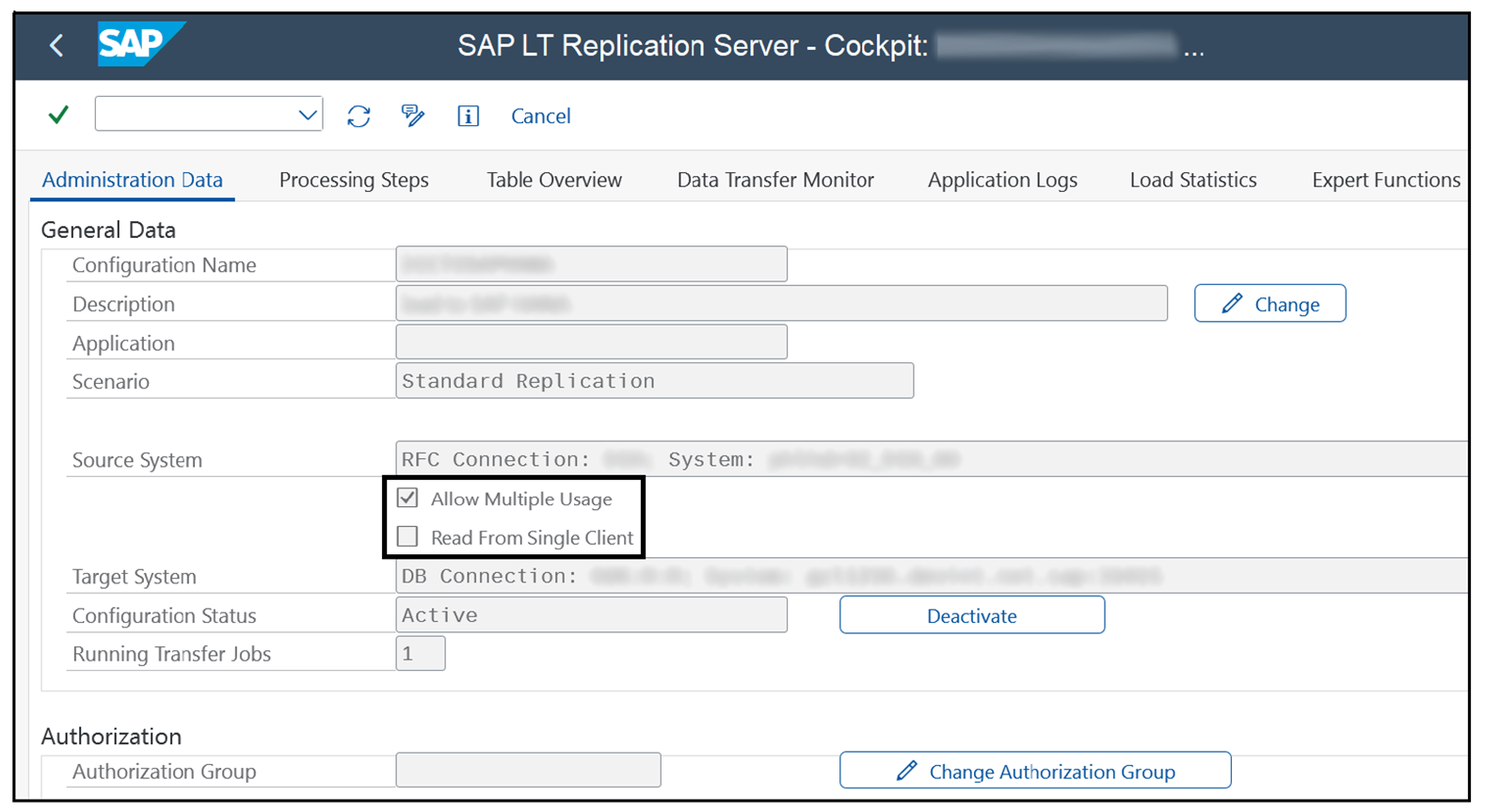
Table Does Not Exist or Unknown
When a table is triggered for replication via SAP LT Replication Server, SAP LT Replication Server creates a synonym and physical target table. When this synonym or physical table is not available for SAP LT Replication Server to load data into, you can expect to see the following error: Table does not exist or unknown.
When you come across this error, make sure the synonym and target table do exist in the respective schema in the target database. You can access the synonym information from the Table Overview tab in Transaction LTRC or from the Participating Objects tab in SAP LT Replication Server, based on your DMIS version.
Communication Issue
When a planned or unplanned outage occurs in a source and/or target system, it also affects SAP LT Replication Server's operations due to its inability to access those systems. In such situations, it's natural to encounter communication issues between SAP LT Replication Server and the source/target systems, leading to replication failures.
When the source and targets are back online and operational, SAP LT Replication Server will automatically try to reestablish connections, allowing replications to pick up from the point at which they were interrupted. For planned maintenance activities (such as changing the hostname of the source), it's important to adjust the relevant RFC connections with the new system details after the outage. This adjustment is necessary to prevent communication issues from arising.
Cannot Create Logging Table /1CADMC/XXXX; Table Exists with Different Structure
A logging table holds key columns of the application table along with other standard logging table columns. Logging tables are typically named based on sequence numbers (marked by XXXX in the logging table /1CADMC/XXXX, and also known as IDENT). These sequence numbers are assigned based on contents from table IUUC_LOG_APPLTAB in the source system and table IUUC_LOGTAB_ID in SAP LT Replication Server. It is common to see SAP LT Replication Server using the same name for a logging table when replicating data from an application table in source to multiple target systems. However, in certain situations, it is also possible that the same logging table name is assigned to a different application table. In such scenarios, you see the Cannot Create Logging Table /1CADMC/XXXX; Table Exists with Different Structure error. When you come across this error, follow these steps:
- Check table IUUC_LOG_APPLTAB in the source system and table IUUC_LOGTAB_ID in SAP LT Replication Server to see if the IDENT was previously used in another table and is obsolete. If it is obsolete and no longer used for replication, remove the entry from table IUUC_LOG_APPLTAB in the source system and start the replication in SAP LT Replication Server.
- If there is a duplicate entry in IUUC_LOGTAB_ID in SAP LT Replication Server for both the original table using the IDENT and the new table, remove the entry for the new table from table IUUC_LOGTAB_ID in SAP LT Replication Server and start replication again in SAP LT Replication Server.
- If IDENT is not obsolete, which means the related source table is currently being replicated by SAP LT Replication Server, then sort the LOGTAB_NAME column of table IUUC_LOG_APPLTAB in the source system in descending order, and make note of the largest IDENT
- Execute Transaction SNRO in SAP LT Replication Server. Then enter “IUUC_SHDW” for the Object and click Display the Intervals. Change the interval to a larger value than the one noted in the previous step.
- Start the replication from SAP LT Replication Server.
With these modifications, SAP LT Replication Server will assign the new IDENT value for the logging table and triggers, ensuring successful replication.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server: The Practical Guide by Prathyusha Garimella and Shashidhar Garimella.



Comments