SAP Best Practices for SAP S/4HANA have been made available to allow for quick implementation of core standard based organizational structures and process flows.
They contain pre-configuration and optional demo data content that can easily be activated in a system using the respective solution implementation tools. SAP Best Practices align to SAP S/4HANA versions and span several countries and languages.
In the area of supply chain management, and warehouse management specifically, the SAP Best Practices content is provided for both embedded and decentralized EWM. Embedded EWM-based processes will be used and described within this chapter.
A subset of the preconfigured processes for embedded EWM forms the basis for a variety of custom developments that we will explain in the following sections. You can certainly try out and use the examples within your self-configured processes, but they might have to be adapted first to the individual situation. However, if you have the opportunity to install SAP Best Practices for EWM in your system before you start programming, we recommend doing so, because it forms the basis upon which our custom developments were built and tested.
We will now look at the functional scope of the SAP Best Practices for embedded EWM and present an overview of the enhancements within the scope items, which will be described in much detail in the following sections. Last but not least, we will provide some information on how to get your system prepared to reenact the processes and enhancements.
Functional Scope of SAP Best Practices for Embedded EWM
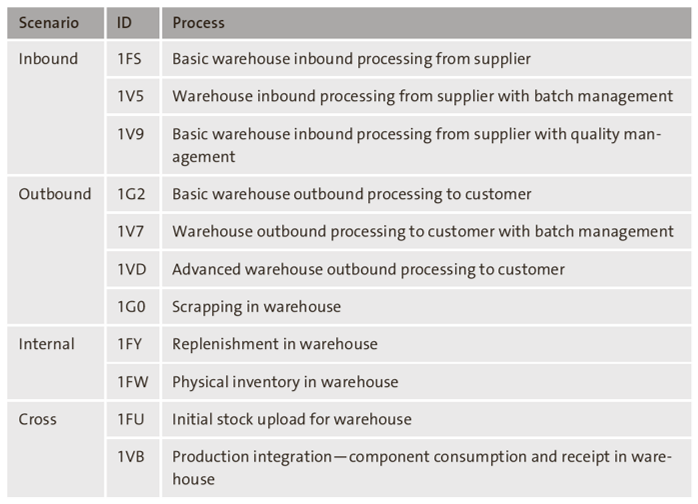
SAP Best Practices for SAP S/4HANA represent a library of scope items. The contained scope items for embedded EWM include typical warehouse management scenarios of inbound, outbound, and internal operation within one warehouse number. Fundamental settings have been included for organizational structure, master data, and resource management, as well as for integration with the SAP S/4HANA system, which is critical in ensuring the operation of all processes. The 11 scenarios and processes shown in the table below are available in SAP Best Practices for embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA 2022. During activation of the SAP Best Practices solution, items from this set of processes can be chosen for custom installation.
In the following paragraphs, we will provide you with an overview of SAP Best Practices for embedded EWM in terms of organizational structures and integration with other SAP S/4HANA functionality—predominantly materials management and logistics execution.
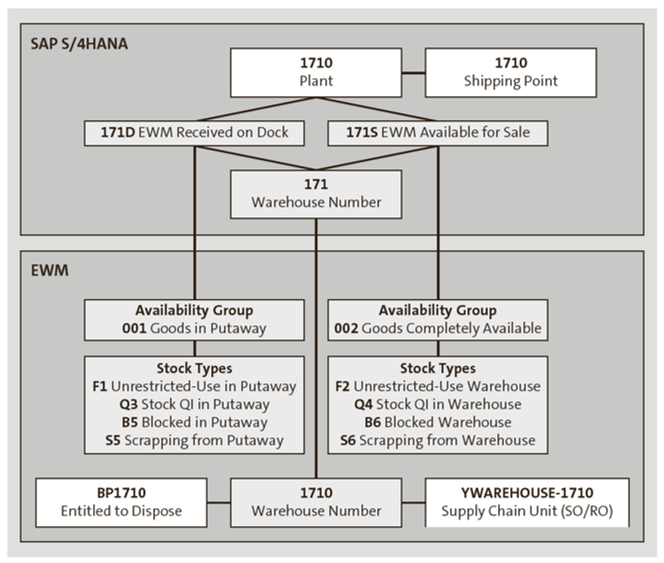
The figure below provides an overview of the organizational structures used for the integration with SAP S/4HANA. The SAP S/4HANA warehouse number is directly linked to the EWM warehouse number, whereas the SAP S/4HANA storage locations are mapped to EWM stock types via availability groups. When setting up the SAP S/4HANA integration, you will be able to choose the organizational structures of the SAP S/4HANA modules that you would like to integrate with the EWM warehouse number.
We recommend reading the How-To Guide for Basic Settings for SAP EWM in SAP S/4HANA hen setting up the SAP S/4HANA to EWM integration configuration for using embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA. It contains valuable information on configuration of qRFC communication, warehouse creation, and integration into the enterprise organizational structure. Alternatively, search for “Pre-Activation Settings for Embedded EWM Scope Items” in the SAP Help Portal (https://help.sap.com/).
The next figure shows the organizational structure of warehouse number 1710 as used in the individual processes. Warehouse number 1710 is assigned a variety of storage types that are used for the different material movements within the processes. These primarily differ by product size. Inside the storage types you can find storage sections, which again are broken down by product demand—namely, fast, medium, and slow movers. Doors, staging areas, and work centers can be found for inbound and outbound operations.
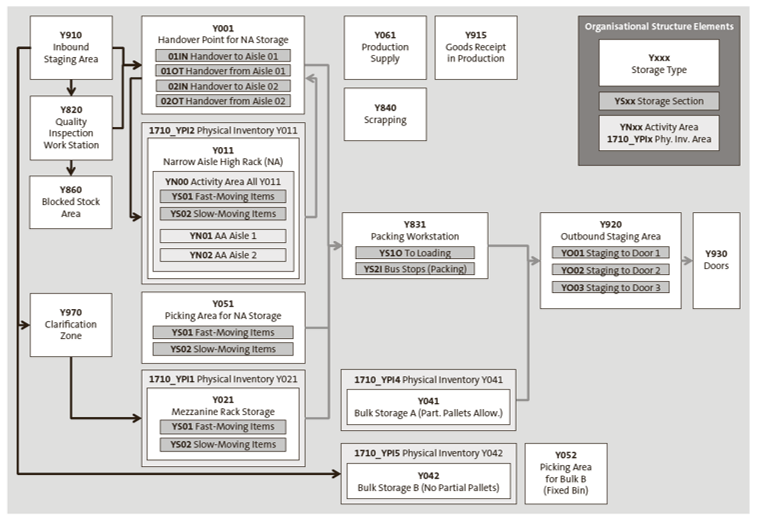
Warehouse number 1710 also includes storage types for clarification and scrapping. The use of storage types is documented in detail in the process descriptions of the various processes, which are included with the documentation of the respective SAP Best Practices scope items.
You can find additional information for the use of master data and settings for resource management in the test cases of SAP Best Practices scope items as well as individual step-by-step process descriptions. They contain detailed information on the procedures and transactions used for each of the 11 available scope items. You can find them in the Process Navigator by SAP on the SAP for Me platform at https://me.sap.com/processnavigator. You need registration with SAP (S-User) to be able to access this content.
Let’s get an overview of the inbound functionality of the EWM system used in the scope items for embedded EWM:
- Delivery processing
- Creation of inbound delivery in SAP S/4HANA with purchase order reference
- Creation of inbound delivery in EWM with purchase order reference
- RF-based receiving of handling units
- (Partial) goods receipt posting on handling unit level
- Warehouse logistics
- Automatic warehouse task creation for inbound delivery via PPF action
- Process-oriented storage control
- Layout-oriented storage control
- Usage of quality inspection work center
- Printing of warehouse order
- Warehouse task confirmation with difference correction (supplier/warehouse)
- Warehouse task confirmation with put-away physical inventory
- Warehouse task/warehouse order confirmation with RF
- Quality inspection
- Warehouse task creation as follow-up activity of quality inspection usage decision
- Stock management
- Automatic posting change from received on dock to available for sales stock
- Automatic posting change from quality to un-restricted use stock
- Automatic posting change from quality to scrap stock
Let’s also look at the functionality of outbound scope items, as follows:
- Delivery processing
- Creation of outbound deliveries in SAP S/4HANA with sales order reference
- Batch selection in outbound delivery item
- Printing of outbound delivery note
- Warehouse logistics
- Manual warehouse task creation via PPF action
- Automatic wave assignment via PPF action (advanced)
- Process-oriented storage control
- Layout-oriented storage control
- Warehouse order creation with packing profile
- Picking partial handling unit quantities
- Packing and confirmation of pick handling units as ship handling units via RF
- Printing of shipping labels
- Warehouse task confirmation via RF
- Warehouse task confirmation with exception handling for differences in picking and packing
- Movement of handling units to staging area
- Controlled loading of handling units to transportation unit
- Shipping
- Manual creation of transportation units (advanced)
- Manual assignment of doors
- Manual assignment of deliveries to transportation units
- Printing of loading lists
- Stock management
- Manual goods issue posting for outbound delivery
- Manual goods issue posting for transportation unit (advanced)
The internal warehouse processes use the standard functionality as provided for inventory procedures (periodic and cycle counting), scrapping, and automatic replenishment.
Overview of Enhancements within the Scope Items
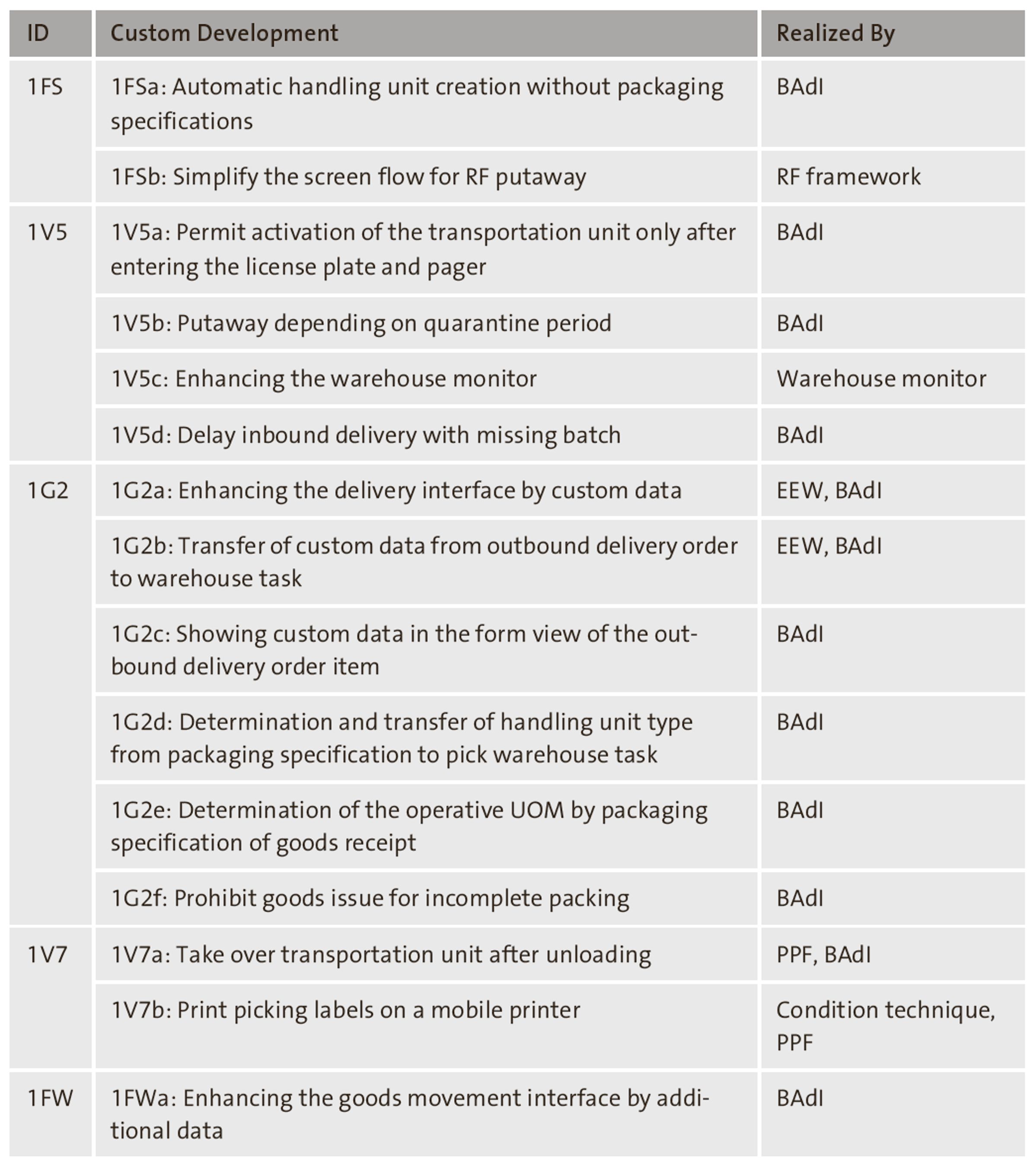
The basic inbound and outbound scope items of the SAP Best Practices for embedded EWM already contain much of the core warehouse management functionality, focusing on delivery processing, SAP S/4HANA integration, and a variation of different putaway and picking procedures. Further scope items then broaden the scope of warehouse management to include the advanced functionality of batch management, shipping and receiving, and more complex warehouse logistics supported by the use of wave management and quality management. We have tried to position the example enhancements within the scope items accordingly. The table below gives an overview of the enhancements that we present in this chapter, indicating the framework or enhancement technique used for each development.
Installation of SAP Best Practices for Embedded EWM
For setting up the SAP Best Practices scope items in an on-premise EWM system, you will need to use the solution builder (Transaction /N/SMB/BBI). We recommend following the Administration Guide to Implementation of SAP S/4HANA 2022 with SAP Best Practices, which you can find in the help portal for SAP S/4HANA at https://help.sap.com/. The guide will take you through prerequisite settings, implementation, and upgrade procedures for loading, scoping, and activation of SAP Best Practices in your on-premise system. There is also a dedicated section on SAP S/4HANA–based scope items that you will need to activate on top of the EWM scope items so as to enable end-to-end processes.
Activating an SAP Cloud Appliance Library Instance
The fastest and easiest way to run SAP Best Practices processes and reenact the provided development examples would be for you to activate an SAP Cloud Appliance Library instance. This will specifically be easy if you already have an account at one of the following available cloud service providers:
- Amazon Web Services
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform
If you do not have an account with one of these providers yet, you might consider getting a trial account for a limited time, which often comes with a free budget allowing you to run the appliance actively for a decent number of hours.
With your cloud provider’s account available, it should be fairly easy to create a trial instance of the latest SAP S/4HANA version. Go to http://cal.sap.com and explore the available fully activated appliance templates for SAP S/4HANA. To create an SAP Cloud Appliance Library instance, you will need a valid SAP ID before selecting your cloud provider, and then will need to specify your account credentials for the provider accordingly. Thereafter, you should be ready for the instance activation. If you run into activation issues, check the provided error log. You might likely need to request a parameter change at your cloud provider to fit the requirements of the SAP recommended virtual machine (VM) sizes. Once this is settled, it will only take a few hours before you have an SAP Cloud Appliance Library instance available for activation and connection. Make sure to suspend the instance when not actively using it to save some budget. Check out the SAP Cloud Appliance Library support page for further information and for how-to videos about instance activation.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book EWM with SAP S/4HANA: Architecture and Programming by Peter Zoellner, Robert Halm, Daniela Schapler, and Karen Schulze. Peter joined SAP Consulting in 2001 and has worked for both domestic and international customers from numerous industries, specializing in logistics execution and SAP EWM since its first introduction to the market. Robert is the head of Portfolio Management at prismat, where he focuses on mobile applications and SAP HANA solutions, especially for warehouse processes. Daniela is a solution architect at SAP SE. She joined SAP SE in 1996 as a developer in the area of logistics execution, following her study of physics at the Universität Tübingen. Karen has worked as a developer and consultant in the area of SAP EWM for more than 14 years.



Comments