The Access Logs section offers access to different logs created in SAP Integration Suite.
There are two tiles available: the Audit Log and System Log Files. Whereas the audit log is more relevant for auditing purposes, the provided system logs are mainly required for error analysis.
Monitor Audit Log
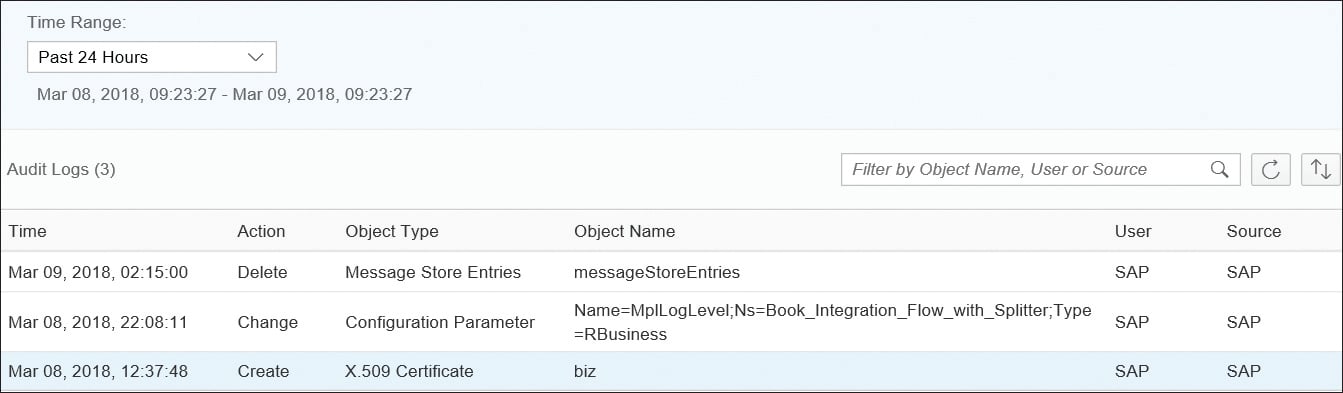
Audit logs are security-relevant records. SAP Integration Suite needs to log all system changes in the SAP Integration Suite tenant. The changes logged are configuration changes, deployments, or deletions of security artifacts; log level changes; and so on. All those changes are logged in the audit log. The monitoring dashboard offers access to the audit log via the Audit Log tile (refer to the figure below).
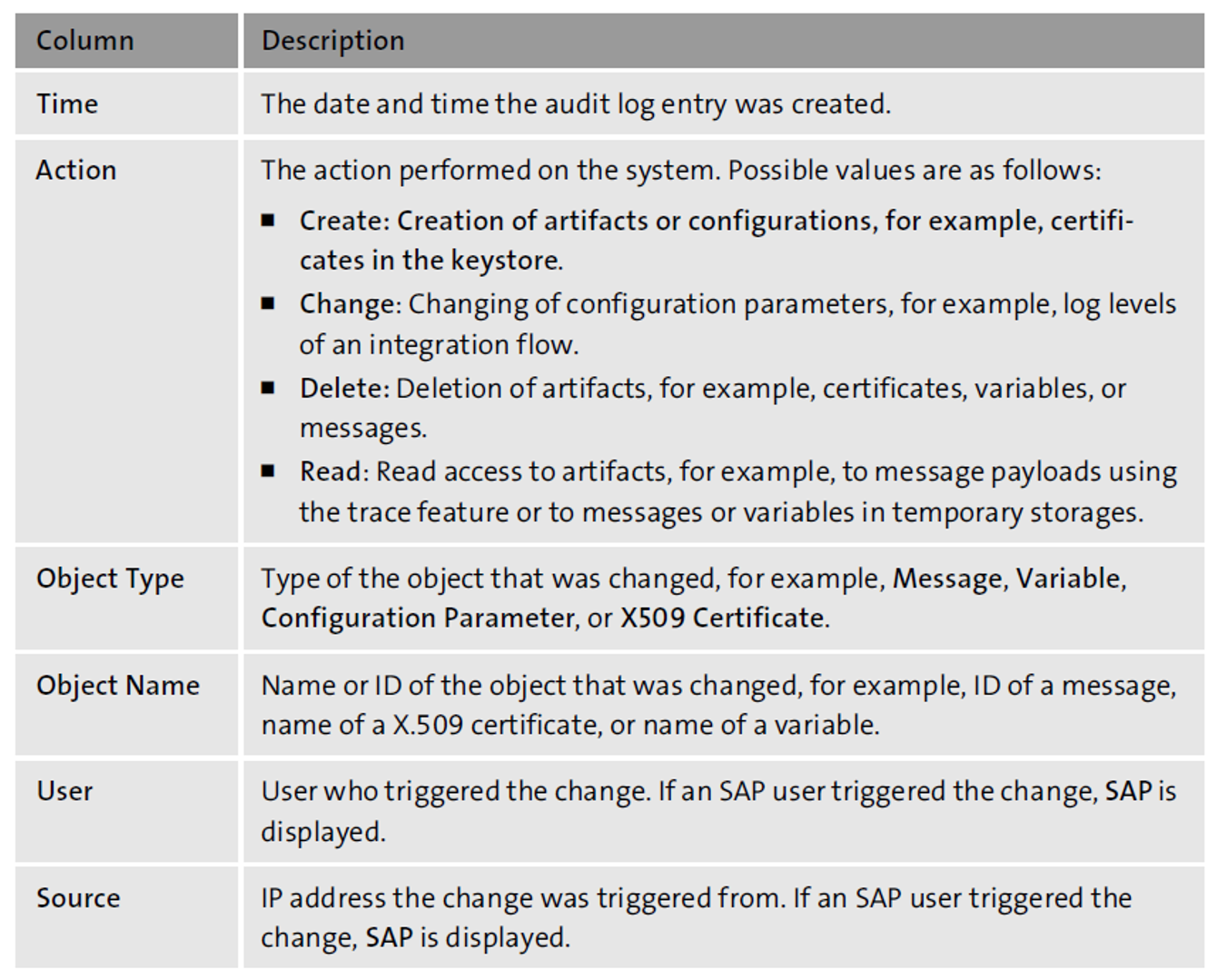
Selecting the Audit Log tile opens a table in a new screen showing all audit logs of the last hour (see the two figures below). However, you can adjust the Time Range at the top of the table to see audit logs for a longer time period. In the second figure, for example, you see the audit logs for the Past 24 Hours. There’s a table a little farther down which provides a detailed description of the attributes for audit log entries.
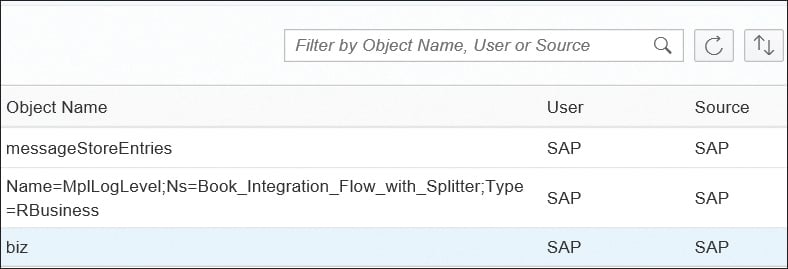
The retention time of audit logs is 30 days, after which the audit log is automatically deleted.
You can sort the entries using the Sort icon or filter by Object Name, User, or Source using the Filter field at the top of the table.
Now let’s look at the second tile in the Access Logs section, which provides access to system logs.
Check System Log Files
Sometimes, the error messages shown in the message processing log aren’t sufficient to fully understand the root cause of an error or SAP support requires detailed information for analyzing an error. In such cases, you need to have a look into the system logs written during message processing on the runtime node. The System Log Files tile provides access to those technical system logs.
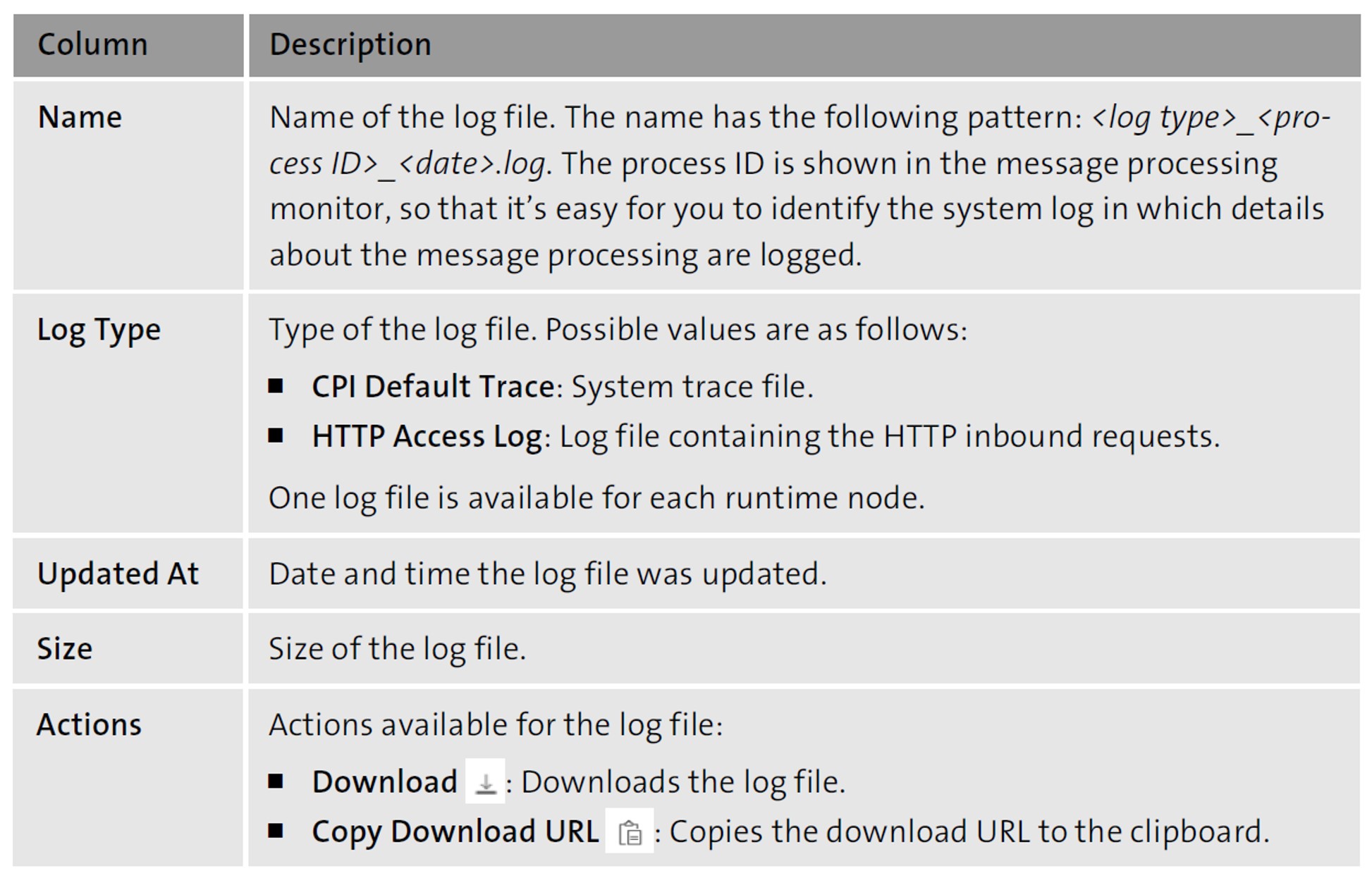
Selecting the System Log Files tile opens a table containing the most important log files of the runtime nodes running in your cluster (see below) in the Log Files tab. The table below provides a detailed description of the attributes of the system log files.
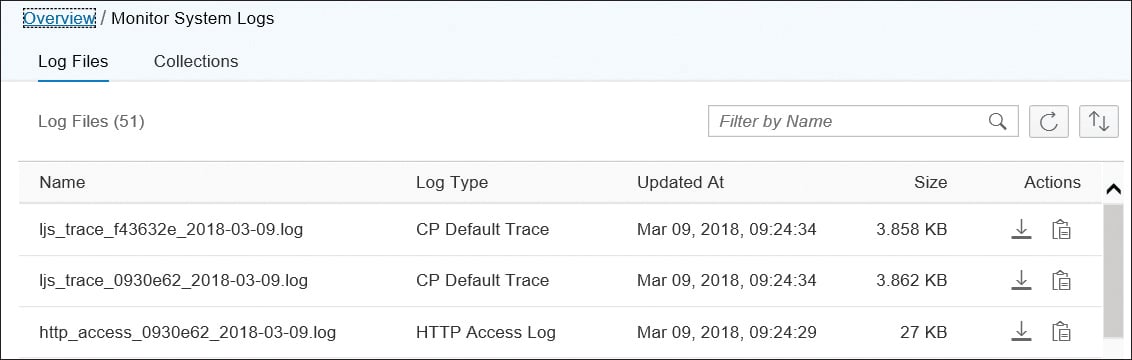
The retention time of the system log files is seven days. After that, the system logs are automatically deleted.
You can sort the entries using the Sort icon or filter by Name using the Filter field at the top of the table.
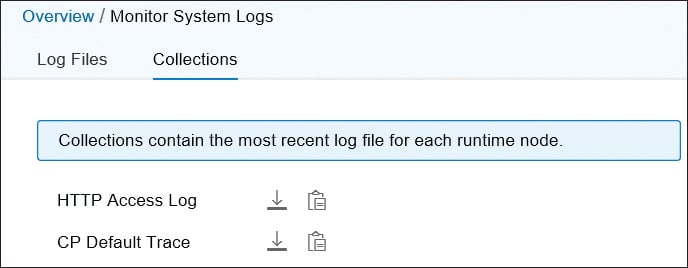
In the Collections tab, you can access collections of the system log files (see below). You can download the collections as an archive or copy the download URL. Downloading the collection, you get a *.zip archive containing the latest log files.
Conclusion
Logs are important, for example, when specific errors need to be analyzed that occur during runtime processing. Often detailed logs are requested by SAP support to analyze specific error situations. Therefore, it’s important to know which logs are available and what they contain. This blog post introduced you to the two logs available for use in troubleshooting. Learn more about SAP's security offerings here.
For more on SAP Integration Suite, check out this post.
Learn SAP Integration Suite in Our Rheinwerk Course!
Get to know SAP Integration Suite with this in-depth course! Get an overview of the suite and its capabilities, learn to design integration flows, work with adapters, build and manage APIs, and monitor your integrated system. This upcoming course in September and October is live on the web and will teach you all you need to know about these topics. Get access to course recordings by clicking the banner below.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book Cloud Integration with SAP Integration Suite: The Comprehensive Guide by John Mutumba Bilay, Shashank Singh, Swati Singh, Peter Gutsche, and Mandy Krimmel.




Comments