SAP S/4HANA brings about many innovations, including multiple upgrades to sales functionality over SAP ERP Sales and Distribution.
Most of today’s pain points in this area relate to the lack of real-time analytics and visibility across the entire order fulfillment process. In this blog post, you’ll learn how innovations such as the sales order fulfillment cockpit can help internal sales order representatives significantly in performing more efficient and effective work.
Other areas of innovations are related to the condition contract settlement, which will enable enterprises to be more flexible due to the more rule-based and flexible architecture of the solutions.
Data Model Simplification
In SAP S/4HANA, various existing status tables have been eliminated, and all fields under these tables have been moved to the corresponding header and item tables for sales documents, deliveries, and billing documents. The document flow table has been simplified as well. Redundant document and rebate index tables have also been eliminated.
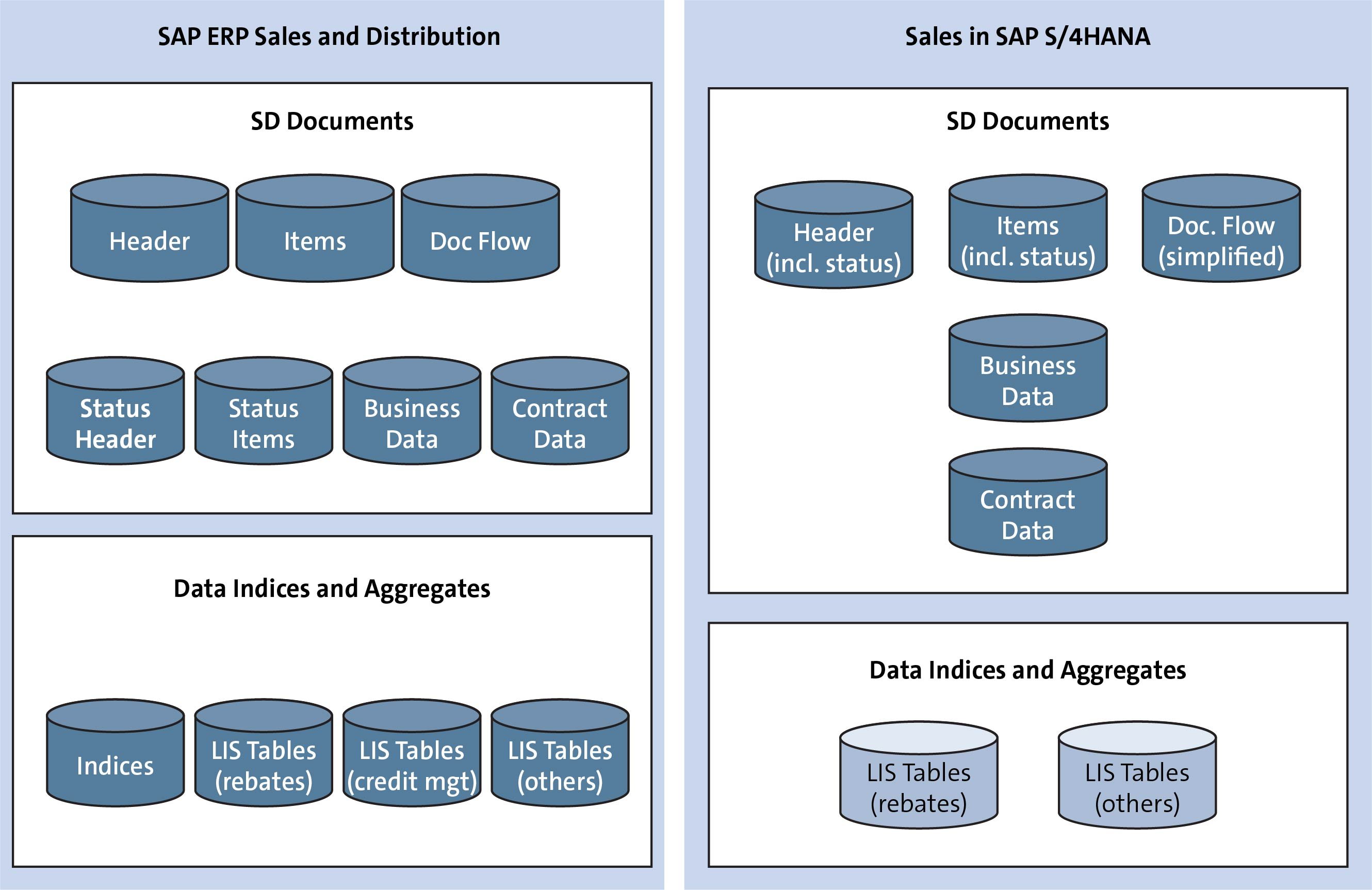
With the changes in the data model, SAP S/4HANA offers the following key benefits:
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO) due to data model simplification
- Reduced memory footprint (e.g., simplified document flow, elimination of index tables, fewer aggregates)
- Increased performance of SAP HANA queries and code pushdown (one SELECT statement instead of two SELECT statements; easier join for header/items, including status and business data)
- Increased robustness of rebate processing (no redundancies due to aggregates)
- Faster business outcomes with reduced operational cost
- Increased competitiveness with integrated, fast, and flexible business processes
- Higher employee productivity with focus on value-added tasks
Sales Order Fulfillment and Replenishment
SAP S/4HANA Sales enhances the entire sales process from order entry to delivery and billing, providing real-time visibility into order status, inventory, and customer satisfaction. Using the SAP S/4HANA Sales Order Fulfillment Cockpit, powered by SAP Fiori, sales representatives can quickly identify and resolve issues across the sales process via a single dashboard. Additionally, SAP introduces an advanced intercompany sales process and the ability to sell from stock with valuated goods in transit, which we will discuss alongside the cockpit functionality and key analytics for improved order-to-delivery performance monitoring. We’ll discuss these functionalities in more detail in the following sections.
Advanced Intercompany Sales
Advanced intercompany sales has been introduced as a streamlined and integrated approach to handling transactions between different entities within the same organization. It facilitates an automated end-to-end integration of the intercompany process, and by creating the sales orders, deliveries and customer invoices, it will create the follow-on documents for all affiliates via value chain monitoring. It assures financial value chain integrity and transparency by full insight into the financial flow among the affiliates and at the group level. From a logistical perspective, it optimizes stock levels by enabling real-time inventory synchronization among all companies.
As shown in the figure below, this process takes place as follows:
- An external customer creates a purchase order (1).
- The sales organization in the selling company generates a standard sales order (2), which initiates the ordering of goods from another company (the delivering company). This sales order (2) drives the intercompany sales process.
- After the sales order (2) is saved, the system automatically generates an intercompany purchase order (3) in the selling company for all relevant items. This step enables cost tracking within product costing. If goods are sourced from multiple plants, multiple purchase orders are created. The quantity of items must be at least partially confirmed at the delivering plant (e.g., plant 1710).
- At the delivering company, the system then automatically creates an intercompany sales order (4) for each purchase order.

- The delivering company prepares an outbound delivery (5) linked to the standard
sales order 2 and ships the goods directly to the external customer specified in the
original sales order from the selling company. - Once the physical goods are shipped, the system records them as “stock in transit” (6) at the delivering company’s plant, such as plant 1710. This step allows the billing team to generate an intercompany customer invoice (A) while ensuring that stock in transit is properly valued.
- Control dates within the outbound delivery (5) determine when stock in transit is recorded, including the goods issue ((7), first lower box) at the physical plant and goods receipt ((7), second lower box) at the transit location. The valuation of stock in transit within the selling company (steps (7) and (8)) enables smooth controlled transfer of goods, allowing revenue recognition based on IFRS 15 requirements.
- After creating the intercompany customer invoice (A), or once goods receipt ((7), second lower box) is posted in the selling company, the system automatically generates an intercompany supplier invoice (B).
- Finally, the selling company issues the customer invoice (C) once the goods are shipped from the delivering company, completing the intercompany transaction.
Sell-from-Stock Process with Valuated Stock-in-Transit
The sell-from-stock process with valuated stock-in-transit (VSiT) allows companies to sell goods that are in transit between locations while having a precise valuation of the stock. For better tracking and monitoring, you can also use the Monitor Value Chains app.
As shown in Figure 5.3, the process can be summarized as follows: When a customer creates a purchase order (1) for goods that are currently in transit between locations, the selling company creates a sales order (2) and prepares an outbound delivery (3) to ship the goods to the customer. Following the necessary warehouse activities, the goods issue is posted (4), moving the stock to a valuated stock-in-transit segment, while the ownership of stock still remains with the selling company. Based on the external transfer of control date, once the goods issue is posted from the valuated goods in transit (5), the selling company will no longer have control of the stock. Finally, a customer invoice (6) can be generated with reference to the outbound delivery.

Sales Order Fulfillment Cockpit
SAP S/4HANA enables users to monitor, manage, and collaborate on sales orders due for shipping and invoicing, ensuring that customer and company agreements are fulfilled accurately and on time. The Sales Order Fulfillment Cockpit allows sales representatives to visualize issues across the entire end-to-end sales process on a unified dashboard, enhancing their ability to manage and collaborate on order-to-delivery performance and address issues related to invoicing, compliance, and trade regulations.
Note: In addition to the Sales Order Fulfillment Cockpit, SAP S/4HANA offers the Create Sales Orders SAP Fiori app, which provides an enhanced user experience with a simple and intuitive user interface that has straightforward navigation to other relevant sales applications. Additionally, you can import sales orders from a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet through the Import Sales Orders app.
The cockpit introduced the Sales Order Fulfillment – Analyze and Resolve Issues app in SAP S/4HANA, which offers the following business benefits:
- Enables visibility into order fulfillment
- Provides internal sales representatives the ability to focus on critical issues/exceptional cases
- Combines analytical insights with operational actions to allow internal sales representatives to run actions directly and track the progress at any point in time
- Improves collaboration with internal and external contacts to resolve issues
With the Sales Order Fulfillment – Analyze and Resolve Issues app, companies can reduce their order-to-cash cycle time, increase their service level, and reduce outstanding payments. In the traditional SAP ERP system, the internal sales rep must check multiple reports for a holistic view of all related processes. Multiple issues in one order can’t be detected easily in one step, creating a higher risk of undetected exceptions. Problem-related communication and decisions can’t be tracked in the system, and reports need to be run multiple times.
In the Sales Order Fulfillment – Analyze and Resolve Issues app, the user can immediately view all the sales order fulfillment issues on one screen categorized by sales order issues, delivery issues, supply chain issues, or billing issues. The SAP Fiori UX enables the user to drill down into each type of issue and immediately make corrections through the sales order fulfillment cockpit.
The figure below shows the sales order fulfillment cockpit with the number of issues for each category and the sales documents details visible.

SAP has continuously improved sales order monitoring by transitioning from rudimentary tracking tools to advanced, real-time, and predictive monitoring systems. For example, you can use the Sales Performance Prediction app to predict sales performance based on predictive models.
The Sales Order Fulfillment – Analyze and Resolve Issues app allows users to filter the reporting results based on product marketability status and dangerous goods status, providing better analysis and problem-solving capabilities. Some of these latest improvements include the following:
- A central entry point for order resolution optimization during analysis and order fulfillment monitoring
- Direct connection to the Track Sales Order Details app in SAP Fiori for a deep dive into the sales order status
- Immediate highlighting of issues, such as incomplete data, delivery issues, invoicing issues, and trade compliance issues
Next to the sales order fulfillment cockpit, several sales key performance indicators (KPIs) are provided and fully integrated into SAP Analytics Cloud. These include insights into the after-sales process with additional service key figures for a comprehensive view of the order-to-cash process. This dashboard as well as other templates for sales KPIs are stored and provided in SAP Analytics Cloud.
SAP’s copilot features have been divided into two components: a collaboration manager and a digital assistant. The collaboration manager is designed to facilitate peer-to-peer collaboration, whereas the digital assistant, Joule, incorporates AI to provide enhanced assistance in daily sales tasks (only in public and private cloud). For example, the sales teams can now harness the power of AI to track and resolve sales order fulfillment problems, significantly improving order accuracy and customer satisfaction.
In addition to the improved sales analytics and monitoring, some new enhancements and innovations have been added in the area of sales documents and billing:
- New functionalities have been added to the Track Sales Order app to enable users to do activities such as mass transactions directly from the sales order list or deep dive directly into the sales order from the cockpit.
- Responsibility management for sales documents, which enables users to set up responsibilities for team members in a flexible way, has been integrated with workflow management and situation handling. Workflow management allows the user to model, configure, and administer workflows based on the business rules. Situation handling enables users to set up automation and machine learning rules for urgent business issues for immediate follow-up and action.
- Enhancements have been made to the Manage Sales Orders and Manage Sales Orders without Charge apps, with new capabilities to perform mass changes at the header level.
- In SAP ERP, duplicate sales documents warnings are now given at the sales order entry level. Using the new Manage Duplicate Sales Document app in SAP Fiori, the user can view in a single transaction all sales documents that have a duplicate message, compare the duplicates, and reject duplication if needed. Users can see in a single view the analytics for duplicate documents by sales document category and sales areas level.
- Sales document flows, including transportation statuses, have been updated with SAP S/4HANA. When embedded TM and EWM are used, the sales document flow in SAP S/4HANA can display the full end-to-end flow, including the freight unit and freight order information.
A new functionality is provided for intelligent product proposal, which is an enhancement of the dynamic product proposal functionality during sales order entry. The quantity of the products ordered can also be predicted with the help of an algorithm parameter.
In the area of returns, SAP has introduced advanced returns management and has continuously improved the Manage Customer Returns app in SAP Fiori by adding the following functionalities:
- Returning third-party products to suppliers
- Conducting inspections at customer sites and having materials remain at the customer site
- Processing service materials, BOMs, and full products in the return order and material inspection
- Entering additional inspection fields in the return order and material inspection
Supporting legal requirements related to the refund of services related to a physical product when products and services have been sold together - Assigning batch numbers for items
- Search functionality for the reference document (sales order, invoice) based on the delivery number
- Improvements in the process flow diagram by adding the return purchase order
Advanced returns management for customer returns enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves overall customer satisfaction. With advanced returns management, you can handle returns to the warehouse, returns to the counter, and direct shipment from the customer to the vendor, and at the same time, you can refund the customer at different times during the process.
Several new apps have been delivered in the area of scheduling agreements:
- Manage Sales Scheduling Agreements: In this new SAP Fiori app, the user can view and display all scheduling agreements according to the criteria entered by the user, while at the same enabling the user to drill down into the details and make corrections and follow-up actions.
- Import Sales Scheduling Agreements: In this new SAP Fiori app, the user can create sales orders from spreadsheets (e.g., Microsoft Excel).
- Sales Scheduling Agreements – Product Demand: In this new SAP Fiori app, the user can view and display customer demand for products and demand fluctuations over time.
- Assign Sold-To Party: This new SAP Fiori app allows the user to assign a relevant sold-to party to a supplier unloading point. The app provides a user-friendly setup of master data, compared to the original customizing settings in SAP ERP.
- Manage Delivery Scheduling Process: This app will allow the user to manage and monitor the delivery process for scheduling agreements.
Enhancements and new features for billing and invoicing include the following:
- Upload functionality of billing document requests via Microsoft Excel for omnichannel convergent billing, using the Manage Billing Document Request app
- Easier scheduling of recurring billing document creation and billing jobs release through the use of rule-based data selection
- Enabling users to set relative rules that specify the period for billing
- Enabling users to specify variable date rules, for example, enabling them to bill all the billing due list documents with a billing date before the first of the month on the fifth of the same month
- Enhancements to the Manage Billing Documents app with new functionality to perform billing document split analysis or compare two billing documents and view what has caused the document split
The preliminary billing functionality has been created to allow users to do the following:
- Create a preliminary billing document based in the billing due list.
- Manage preliminary billing documents, for example, to get an overview of all preliminary billing documents or reject/approve these documents.
- Create billing documents based on these preliminary billing documents
- Make changes to preliminary documents, such as changes to prices and text.
- Generate print previews and outputs.
- Schedule billing creation for preliminary billing documents.
An app has also been made available for automated creation of billing documents with reference to the preliminary one.
Down payment processing can be leveraged by adding a specific milestone billing plan into the sales contract, creating a down payment request and releasing the order. With an additional layer or integration, until the incoming financial payment is booked, the order is blocked for delivery.
Through machine learning and RPA, sales orders can be directly created from buying requests, such as PDF files or emails.
Pricing Management
The Manage Customers Expected Price app enables the user to monitor all sales documents in which the customer has set an expected price, to compare values between the customer’s expected price and the net price according to the pricing conditions set up. This allows the user to either accept or decline the customer price. This SAP Fiori app is available for managing incomplete sales orders with price differences with the customer’s expected price, including blocking and releasing these incomplete sales orders.
SAP S/4HANA allows businesses to implement workflows for sales price approvals. This ensures that sales orders exceeding certain thresholds (e.g., discounts, margins, overall price) must go through a formal approval process. You need to set up a workflow for sending the prices to approval with the Manage Sales Price Workflows app. With the Manage Prices – Sales app price, you can control maintenance by defining upper and lower limits for the condition records. At the same time, you can maintain transparency into the import history while uploading the prices from Microsoft Excel.
For managing sales tax, you can use the Manage Tax Rates – Sales app to create condition records for tax rates, similar to pricing master data. Additionally, you can configure user roles to control price elements access to sales documents at the header and item levels.
Omnichannel sales promotions in sales orders are possible by integrating with the cloud solution SAP Omnichannel Promotion Pricing.
Condition Contract Settlement
In SAP S/4HANA Sales, SD rebates are replaced by the condition contract settlement process, followed by the settlement management process. This means that all existing rebate agreements can only be processed up until the end of the validity date and then closed by a final agreement.
Customers with SAP CRM trade promotion management (TPM) who want to integrate their existing TPM scenarios with SAP S/4HANA will have to use SD rebate processing, which has been optimized for the database footprint. Consider the following key differences between condition contract settlement and the SD rebate agreement functionality:
- With condition contract settlement, SAP provides a central solution for customer and vendor conditions. In the traditional solution, all customer rebate–relevant billing documents are stored in table VBOX. For changes that needed to be applied retrospectively, this table will need to be updated through a separate transaction (Transaction VBOF), and all billing documents in this table would be locked at the same time. The other issue is the size of the table; this table could contain millions of entries required for rebate calculation.
- In condition contract settlement, there is no longer any table VBOF equivalent. Rebate settlement-related information doesn’t need to be stored in a table; instead, rebate conditions will be applied instantly. In addition, condition contract settlement enables the user to use multiple data sources for rebate settlements. Traditionally, this can only be done based on the billing documents.
Below shows the traditional SD rebate agreement versus the condition contract settlement.

The key benefits of condition contract settlement are as follows:
- A flexible and state-of-the-art solution for settlement scenarios in which users can determine business volume sources based on flexible and definable criteria that can be configured in Customizing.
- Designed for high performance (with SAP HANA).
- Enables new and innovative rebate scenarios to be set up thanks to its open architecture.
Foreign Trade
SAP S/4HANA for international trade replaces SAP ERP SD foreign trade. SAP S/4HANA for international trade does not replace SAP GTS; with the release of SAP GTS, edition for SAP HANA, the SAP GTS solution can be installed on the same instance as SAP S/4HANA but in a separate client.
Letter of credit, legal control, export control, and preference management in foreign trade/customs aren’t available any longer in the material master; instead, the international trade-based functionalities are used. SAP S/4HANA for international trade offers functionalities for import management and export management. For Intrastat reporting, a customer can leverage the functionality within SAP S/4HANA. Prior to conversion, careful analysis of all currently used foreign trade processes is needed. SAP S/4HANA for international trade covers the basic requirements for trade and customs compared to SAP GTS.
Please note that SAP GTS requires a separate license.
Credit Management and Revenue Accounting
SAP Credit Management (FIN-FSCM-CR) replaces SD credit management in SAP S/4HANA. SAP provides tools to migrate to SAP Credit Management, which contains several elements:
- Configuration data
- Master data
- Credit exposure data
- Credit decision data
On the revenue accounting side, SAP Revenue Accounting and Reporting replaces SD revenue recognition. SD revenue recognition isn’t available in SAP S/4HANA. Instead, SAP S/4HANA functionality should be used that supports the new revenue accounting standard according to International Financial Reporting Standard 15 (IFRS 15) and adopted by local generally accepted accounting principles (GAAPs).
Conclusion
Similar to SAP S/4HANA Finance and the logistics capabilities of SAP S/4HANA, SAP S/4HANA Sales provides a plethora of functionality improvements over SAP ERP capabilities. In this blog post, you were exposed to some of the most important changes to know. With these in mind, what do you think will be the most helpful to you as you transition to a new SAP S/4HANA system?
Learn SD with SAP S/4HANA in Our Rheinwerk Course!
Dig into SD! Understand the organizational structure and master data in SAP S/4HANA. Learn to customize basic and cross-functional settings in SAP S/4HANA, and then focus on SD processes and their configuration: ATP, pricing, sales processing, shipping, and billing. Take a close look at SD simplifications and enhancements to get the most out of your system! Get access to course recordings by clicking the banner below.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book SAP S/4HANA: An Introduction by Devraj Bardhan, Axel Baumgartl, Madalina Dascalescu, Mark Dudgeon, Piotr Górecki, Asidhara Lahiri, Richard Maund, Bert Meijerink, and Andrew Worsley-Tonks. They are are a multinational author team working for IBM, SAP, and Accenture. They have
been working with SAP S/4HANA since its first release.
This post was originally published 4/2020 and updated 3/2025.




Comments