A transportation management system is a software platform that the transportation industry employs to plan, execute, and optimize the movements of goods, including both inbound and outbound shipments.
A transportation management system ensures compliance with regulations and furnishes the necessary documentation. Managing transportation can be complex, expensive, and time consuming, and thus, a transportation management system is a crucial tool for streamlining supply chains. Transportation was once viewed as a distinct business process, but now it is integrated into overall supply chain and logistics management. A transportation management system frequently forms part of a larger supply chain management system.
To deal with the growing complexity and uncertainty of global logistics, businesses must improve logistics processes, enhance services, and increase visibility and control.
A transportation management system provides a holistic perspective of daily transportation operations, encompassing trade compliance data, essential documentation, and the timely delivery of goods and freight. Transportation management system solutions streamline shipping processes, allowing an enterprise to oversee and enhance its transportation operations across various modes of transportation, such as land, air, and sea.
Transportation management systems play a crucial role in modern supply chains, affecting each stage of the process, from planning and procurement to logistics and lifecycle management. A strong transportation management system offers comprehensive visibility, facilitating more effective transportation planning and execution, leading to improved customer satisfaction and increased sales growth. Given the continuously changing global trade environment, having a transportation management system that can assist businesses in successfully navigating complex trade policies and guaranteeing compliance with regulations is vital.
Transportation management systems are primarily employed by businesses that require frequent shipping, moving, and receiving services, such as manufacturers, distributors, e-commerce companies, and retail businesses. Additionally, logistics service providers, including third-party logistics (3PL) and fourth-party logistics (4PL) firms, commonly use transportation management systems to provide logistics services to their clients.
The SAP Transportation Management (SAP TM) application integrates fleet management and logistics management, streamlining the movement of goods across various modes of transportation. In this way, SAP TM enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs.
This solution offers a range of features, including transportation demand management, order consolidation, shipment monitoring and tracking, and transportation spend optimization. Additionally, it facilitates strategic freight procurement, capacity monitoring, freight order management, and transportation planning optimization. Furthermore, SAP TM assists in the management of freight financials through freight settlement and provides analysis and reporting capabilities to make informed transportation decisions.
Employing SAP TM, enterprises can implement a uniform transportation system that results in decreased transportation expenses and increased customer contentment. This software streamlines transportation planning, execution, and cost reconciliation, while also furnishing valuable data analytics to augment the overall transportation process.
As shown in this figure, SAP TM, when used in conjunction with SAP S/4HANA, can be deployed in a variety of deployment and integration scenarios.

The following list describes these options in more detail:
- Internal system or embedded integration: In this first scenario, referred to as internal system integration or embedded integration, SAP TM is directly integrated into the SAP S/4HANA system instance. In this approach, SAP TM can directly access logistics data within the SAP S/4HANA system, thus eliminating the need for data transfers between the systems. This approach eliminates the possibility of redundant data and reduces the effort required for data transfer.
- External system or side-by-side integration: In this second scenario, referred to as external system integration or side-by-side integration, SAP TM is implemented as a separate system. In this approach, master data and transactional data are transmitted from the SAP S/4HANA or SAP ERP system to SAP TM using various techniques for replicating master data. SAP TM, which is a component of SAP S/4HANA, can function as a standalone system in side-by-side scenarios in the following ways:
- SAP TM can be integrated with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) instances that have not yet been converted to SAP S/4HANA, as part of the SAP S/4HANA system.
- In situations with multiple SAP S/4HANA instances in a system landscape, SAP TM can be integrated with each instance.
- SAP TM can be implemented with support packs and released independently of other SAP S/4HANA Enterprise Management applications to accommodate different software lifecycle management requirements. While this option may result in a higher total cost of ownership (TCO), the trade-off might be necessary.
Note: Note that, for additional information on deployment and integration options, we recommend consulting the following SAP Notes: 2714892 - SAP Transportation Management - Deployment Options and 2812981 - Transportation Management and decentralized EWM in same SAP S/4HANA system and client
- Integration options between SAP EWM and SAP TM: Different integration options between SAP EWM and SAP TM are available, such as the following:
- Direct integration of embedded EWM and embedded SAP TM on SAP S/4HANA As shown in the next figure, the SAP S/4HANA platform presents a seamless fusion of embedded EWM and embedded SAP TM modules. This amalgamation facilitates instantaneous communications between the two modules and enables a comprehensive look at logistics operations. By virtue of this direct integration, SAP EWM and SAP TM leverage a unified database, effectively eliminating data redundancy and ensuring data coherence.

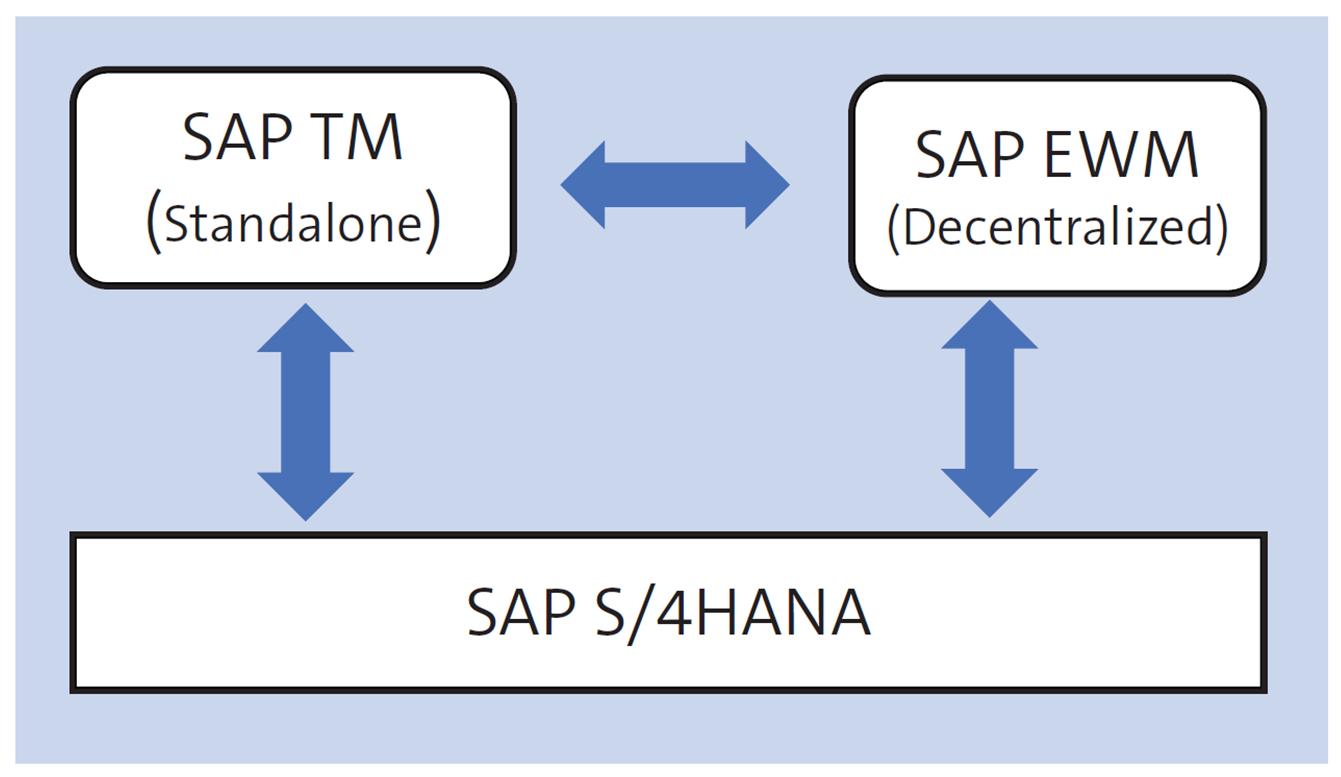
- Integrate decentralized Extended Warehouse Management in SAP S/4HANA (decentralized EWM) and standalone SAP TM: As shown in the below figure, SAP S/4HANA provides a streamlined solution for integrating your decentralized EWM and standalone SAP TM modules. This approach allows for enhanced supply chain management capabilities, enabling your organization to efficiently oversee the flow of goods and optimize logistics processes.
- Integrate decentralized EWM on SAP S/4HANA and embedded SAP TM on SAP S/4HANA: As shown below, SAP S/4HANA provides seamless integration between a decentralized EWM system and the embedded SAP TM modules.

- Indirectly integrate SAP EWM and SAP TM with SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA: As shown in the next figure, in this particular scenario, the SAP EWM and SAP TM systems can be integrated with SAP ERP, and the exchange of data between these systems is facilitated through the SAP ERP system.

Several benefits of this indirect integration approach include the following:
- Leveraging existing SAP ERP infrastructure and investments: By integrating SAP EWM and SAP TM with SAP ERP, a business can make the most of its existing infrastructure and investment in SAP ERP systems. This approach can reduce the cost and effort required to deploy and maintain separate systems for warehouse management and transportation management.
- Streamlined data flow between SAP EWM, SAP TM, and other ERP modules: Indirect integration between SAP EWM, SAP TM, and other ERP modules, such as sales, procurement, and inventory management, can help streamline data flows across different business functions. This approach can lead to improved data accuracy, better decision-making, and reduced errors.
- Improved visibility and control over end-to-end supply chain processes: By integrating SAP EWM and SAP TM with SAP ERP, a business can gain better visibility and control over its supply chain processes. This approach can help identify and address issues quickly, optimize operations, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Management of transportation planning and execution within the context of broader business processes: Integrating SAP EWM and SAP TM with SAP ERP can help a business manage transportation planning and execution within the context of broader business processes, such as order fulfillment and inventory management. This approach can help ensure that transportation plans are aligned with broader business goals and objectives.
- Reduced manual effort and increased efficiency through automation: Indirect integration between SAP EWM, SAP TM, and SAP ERP can help reduce manual effort and increase efficiency through automation. This approach can lead to faster processing times, reduced errors, and improved productivity.
Learn SAP TM in Our Rheinwerk Course!
Your TM training is here! Master the flow of transportation data with SAP S/4HANA. Dive into order management, planning and execution, and transportation charges and settlement. Then explore TM integration with embedded EWM, SAP GTS, and other logistics solutions to get the most out of your supply chain landscape! Get access to course recordings by clicking the banner below.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book Integrating EWM in SAP S/4HANA by Shailesh Patil and Sudhakar Bandaru.




Comments