The master data in SAP EWM is classified into two primary categories.
The first category is external data, which must be replicated from the SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA system into the SAP EWM environment. This external data includes information like material master, vendor master, customer master, plant, and other similar data. The replication of this data is a necessary step in order to ensure accurate and up-to-date data in the SAP EWM environment.
The second category is internal data, which is created exclusively within the SAP EWM environment. This type of data includes storage bin master data and packaging specification master data. These data elements are typically created when setting up the SAP EWM system and are maintained within the SAP EWM system.
Note that the master data replication process from SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA to SAP EWM is a critical component of the overall system setup. This process ensures that the data in the SAP EWM system is consistent with the data in the SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA system. Additionally, the replication process also ensures that any changes made to the data in the ERP or in the SAP S/4HANA system are reflected in the SAP EWM system.
Let’s now consider the different data transfer processes, for SAP NetWeaver deployments, embedded EWM deployments, and decentralized EWM deployments.
Data Transfer for SAP NetWeaver Deployment (SAP EWM 9.5 and Below)
As shown in the figure below to enable the deployment of SAP EWM 9.5 and lower through the SAP NetWeaver SAP Business Suite, the system utilizes the CIF technology to transfer master data between SAP ERP and SAP EWM. CIF is primarily utilized for exchanging data between SAP ERP and SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM).
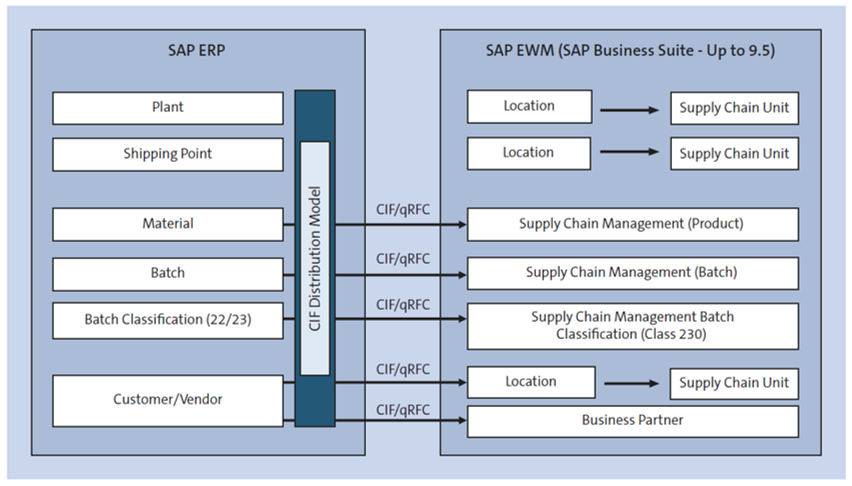
However, in the case of SAP EWM, only master data is transferred from SAP ERP to SAP EWM, and no communication occurs in the opposite direction via CIF.
In contrast, transactional data, such as inbound and outbound delivery documents originating from SAP ERP, are integrated into SAP EWM through the queued remote functional call (qRFC) technology. This method allows for asynchronous communication between the two systems and provides a reliable and efficient way of transferring transactional data from SAP ERP to SAP EWM.
Data Transfer for Embedded EWM
As shown below, in an embedded EWM system, it is not necessary to transfer master data through the CIF. However, note that the transmission of transaction data from SAP S/4HANA to embedded EWM still requires the use of qRFC technology.
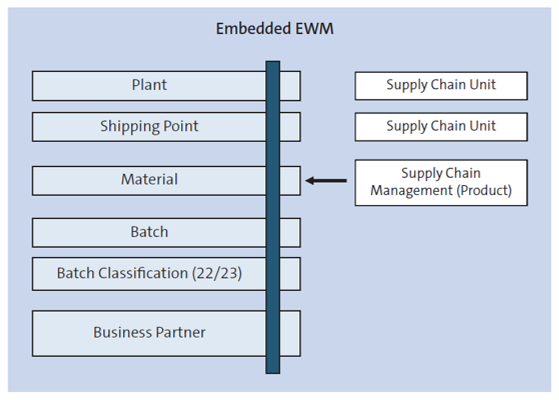
qRFC is a communication method used by SAP systems to transfer data between systems in a reliable and efficient manner. It enables data to be sent in batches, reducing the risk of data loss or errors. In the case of embedded EWM, transaction data includes information about goods movements, inventory updates, and warehouse operations.
By utilizing qRFC, SAP S/4HANA can transmit transaction data to embedded EWM in
a timely and accurate manner. This capability allows for the seamless integration between the two systems, thus enabling real-time visibility into warehouse operations and inventory levels.
Note that, while master data transfer via CIF is not required in embedded EWM, CIFbased data transfers may still be necessary for other SAP components or systems. Therefore, an important step is to evaluate the specific requirements of each scenario and determine the appropriate data transfer method.
Data Transfer for Decentralized EWM
As shown in the next figure, in a decentralized EWM implementation with SAP S/4HANA, the application link enabling (ALE)/IDoc technique is employed for the transfer of material master data from SAP ERP to SAP EWM. Additionally, the data replication framework (DRF) technique is utilized for the transfer of customer and vendor master data, commonly referred to as business partners in decentralized EWM. In contrast, the CIF technique is still utilized for the transfer of certain master data, such as packaging specifications, from SAP ERP to SAP EWM.
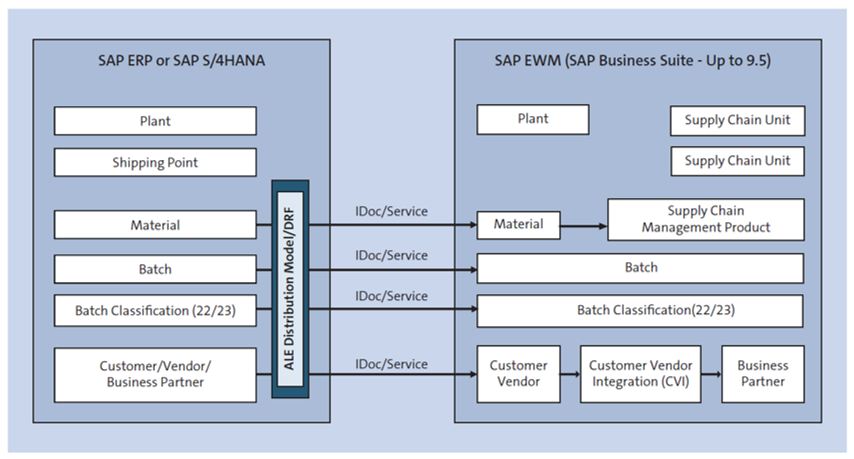
Moreover, certain types of transactional data, such as inbound and outbound delivery documents from SAP ERP, are integrated into SAP EWM through the utilization of qRFC technology. This technology allows for asynchronous communication between the two systems, ensuring that delivery documents are accurately and efficiently transferred from SAP ERP to SAP EWM.
Overall, the combination of ALE/IDoc, DRF, CIF, and qRFC techniques provides a robust and reliable means of integrating SAP ERP and SAP EWM in a decentralized EWM implementation on the SAP S/4HANA system.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book Integrating EWM in SAP S/4HANA by Shailesh Patil and Sudhakar Bandaru. Shailesh stands as an eminent solution architect and subject matter expert at Infosys Limited, showcasing a remarkable and extensive career spanning 19 years of expertise in supply chain management solutions. Sudhakar is a highly accomplished digital logistics execution solution architect with extensive experience in various modules, including SAP EWM, SAP Yard Logistics, and SAP Transportation Management, spanning an impressive career of over 19 years.



Comments