Along with the core SAP S/4HANA solution, a number of peripheral SAP cloud applications provide benefits to financial organizations.
These applications are often in the scope of finance transformation projects, with finance and accounting serving as interested parties in the implementation of these tools. The tools highlighted in this section cover analytics, end-to-end procurement, time and expense management, contingent labor management, and human resources (HR) management.
SAP Analytics Cloud
SAP Analytics Cloud provides a smooth end-to-end analytics experience that simplifies complex processes with one solution. It allows businesses to navigate easily from understanding the data to devising an appropriate plan to taking necessary action to achieve that plan.
Data used in SAP Analytics Cloud can be sourced from a cloud server, a physical server at the customer’s location, or a combination of the two. Regardless of where the data is sourced from, SAP Analytics Cloud provides capabilities for data preparation, what-if analysis, planning, forecasting, visualization, and storytelling. SAP Analytics Cloud is available in two editions.
Embedded Edition
SAP Analytics Cloud, embedded edition comes with no additional licensing or cost, and includes SAP Ariba, SAP Datasphere, SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors, SAP Customer Experience, and SAP Fieldglass. It allows establishing live connectivity to SAP HANA Cloud and supports limited functionality of SAP Analytics Cloud business intelligence (BI), but doesn’t include predictive, planning, or design functionalities.
Enterprise Edition
SAP Analytics Cloud, enterprise edition enables customers to extend analytics beyond the scope of the application data, and to analyze data from multiple sources. There are two options for using SAP Analytics Cloud enterprise edition:
- Exclusively cloud based
- Hybrid of on-premise and cloud solutions
As shown in the figure below, SAP Analytics Cloud includes core capabilities like data connectivity, modeling, and visualization; analytics capabilities like BI, predictive analytics, and planning; and apps like SAP Digital Boardroom.
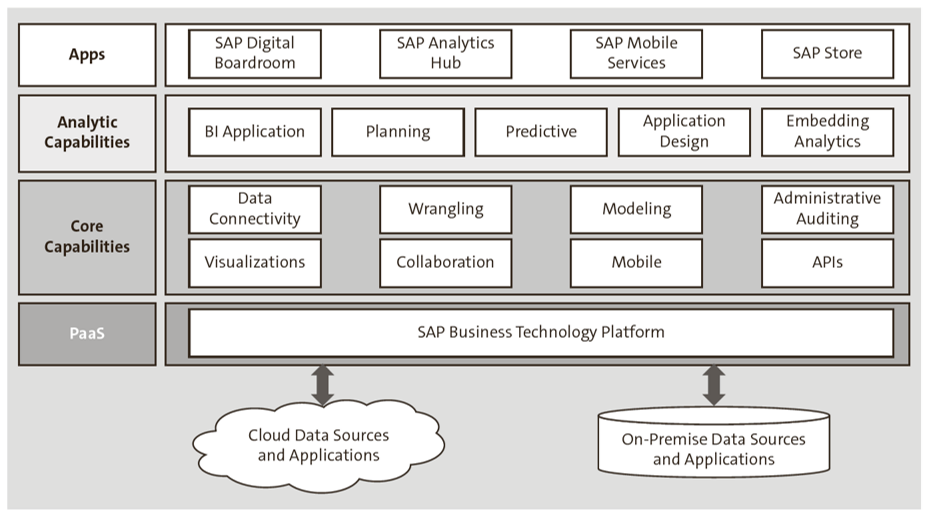
SAP Analytics Cloud brings together these capabilities to analyze all data. It also provides connectivity in two ways: live connection (online) and data acquisition (batch).
Deciding on the type of connection must be made based on the following business needs:
Functional Needs
- Live connection: All data will stay in the source system, which can be either cloud (local data source) or remote (on-premise data source).
- Importing data: All data from the source is copied (replicated) to SAP Analytics Cloud.
Data Privacy
- Live connection: If the business wants full control of data privacy, this is the best choice since data stays in the backend.
- Importing data: Data is replicated into SAP Analytics Cloud’s SAP HANA database, but data is encrypted and fully secured.
Data Volume
- Live connection: There’s no limitation.
- Importing data: There are certain limitations on the volume of data in import connection (for example, 100 columns, 800,000 rows, etc.).
SAP Ariba
SAP Ariba is an end-to-end, source-to-pay, software-as-a-service (SaaS) solution from SAP. In recent years, SAP Ariba has extended capabilities beyond traditional source-to-pay technologies and journeyed into enabling an intelligent digital enterprise utilizing the power of SAP Business Network. The next figure highlights the source-to-pay capabilities and the supporting SAP Ariba modules.
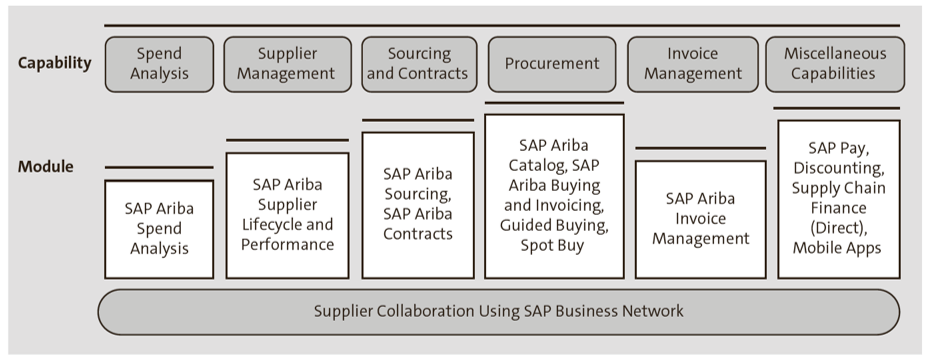
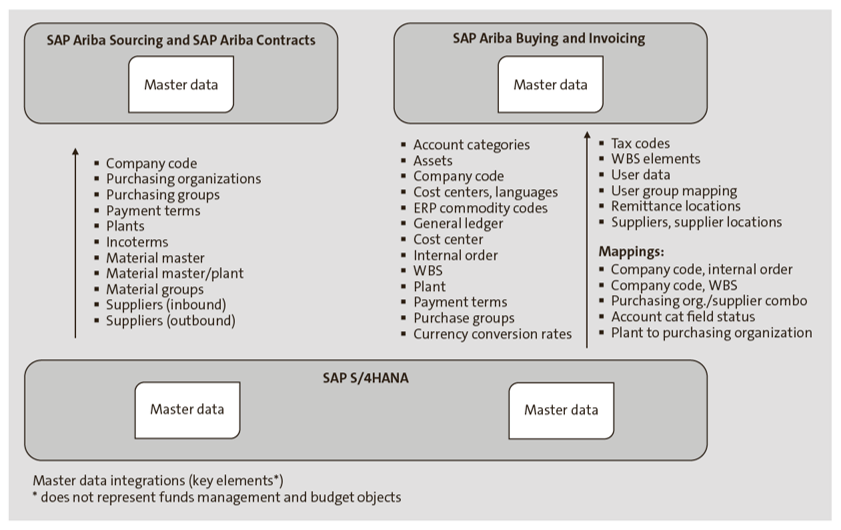
The SAP Ariba suite of products integrates nicely with SAP S/4HANA. The SAP Ariba system is dependent on SAP S/4HANA for master data, including financial master data (company code, cost centers, internal orders, WBS, tax codes, etc.) and procurement master data (purchase organizations, purchasing groups, supplier master data, etc.). Below outlines this structure.
SAP Strategic Sourcing Suite, the bundling of SAP Ariba modules, integrates tightly with SAP S/4HANA and SAP Business Network. Below shows this integration across the three suites to provide a seamless flow of data.
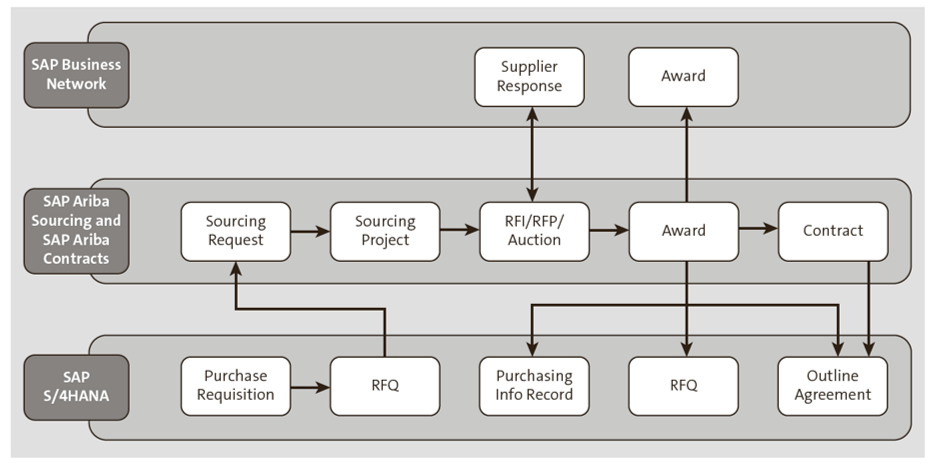
The process begins with a purchase requisition and request for quotation (RFQ) in SAP S/4HANA, and leads to a sourcing request, sourcing project, request for information (RFI), request for proposal (RFP), and/or auction in SAP Ariba Sourcing and SAP Ariba Contracts. Next, SAP Ariba Sourcing and SAP Ariba Contracts integrate with SAP Business Network for supplier response and award. The award results in a purchase info record, RFQ, and outline agreement in SAP S/4HANA, as well as a contract in SAP Ariba Sourcing and SAP Ariba Contracts.
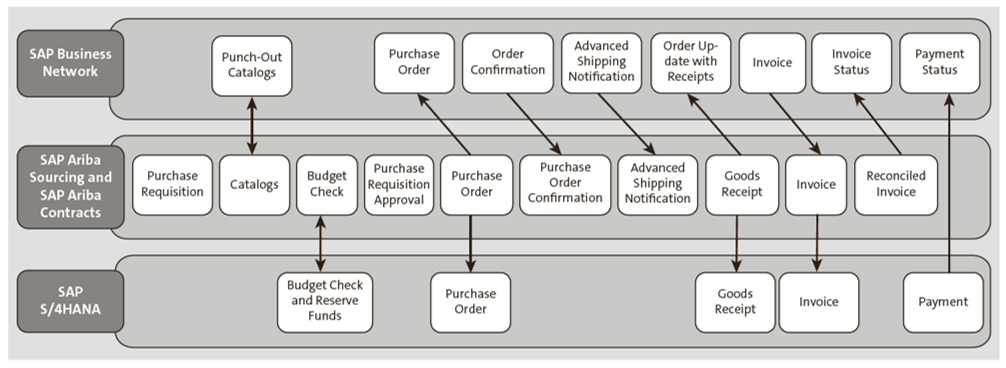
SAP Ariba Buying and Invoicing integrates with SAP S/4HANA for all purchasing transactional data elements, such as purchase orders, goods receipts, and reconciled invoices. Additionally, SAP Ariba Buying and Invoicing integrates natively with SAP Business Network, as shown in this figure.
SAP Concur
Acquired in 2014, SAP Concur is SAP’s primary time and expense solution for clients of all sizes and scopes. Comprised of four core modules (Request and Travel, Expense, Intelligence, and Invoice), SAP Concur helps organizations drive expense and HR policies worldwide to ensure audit compliance and to enhance expense report visibility.
Let’s walk through the key modules.
Concur Request and Concur Travel
Focused on enabling employee travel arrangements, Concur Request and Concur Travel facilitate the entire travel experience. Users can reserve various modes of travel through SAP Concur, and, with travel management system (TMS) connections, book travel through SAP Concur. Employees can submit formal requests to their managers through Concur Request. This increases visibility on expenses before they are incurred by the business. Additionally, depending on client requirements, companies can configure Concur Request to facilitate cash advance processes. Concur Travel can be integrated with Concur Expense to automatically report trip details and expenses for easy report creation. These modules are additionally available via SAP Concur’s mobile application for on-the-go accessibility and visibility.
In Concur Request and Concur Travel, you can:
- Book on the go
- Configure predefined audit rules
- Interface with travel management companies
Concur Expense
Concur Expense is designed to allow companies to easily enforce spending policies, capture receipts, process expense reports, and enable more accurate expense reporting. The expense process consists of expense report creation, approval, and reimbursement. To enable these core processes, SAP Concur provides additional capabilities. Audit and approval triggers can be customized based on expense type, value, etc., allowing for improved policy enforcement. SAP Concur also offers Audit Services, a third-party service that helps the business in review submitted expense reports. SAP Concur offers a service called Expense Pay, which can directly manage the reimbursement process. Card expenses from major providers (American Express, Visa, and MasterCard) can be imported into cardholder profiles, allowing for easy expense creation. Additional key features available through Concur Expense include value-added tax (VAT) calculation, travel allowance configuration, car mileage calculation, and language localization.
Concur Expense contains the following features:
- Electronic receipt autofeed
- Accessible away from the office
- Audit rules visible to the approver
Intelligence
Intelligence, SAP Concur’s analytical tool, is powered by IBM Cognos Analytics, and allows for various standard and custom report generation to provide clients with key expense reporting capabilities. Reporting access is given by group, allowing for easy separation of reporting capabilities within the organization.
With Intelligence, you get the following features:
- Facilitated connections to all data sources
- Prebuilt reporting tools
- Budget control with notification
Concur Invoice
Concur Invoice allows for the management of business spending from purchase requisition through payment processing. Key features include standard invoice dashboards and automated employee and card payments.
Through Concur Invoice, you have the following features:
- Automated payment to employees and credit cards
- Prebuilt standard dashboards
- Reduced cost and gained control of payment
SAP Concur can integrate with a client’s core financial systems in various ways, depending on their software stack. SAP integration with SAP Concur solutions (ICS) enables SAP Concur integration with on-premise SAP ERP and on-premise SAP S/4HANA. For the purposes of this discussion, we’ll focus on ICS. If, however, it’s determined that ICS isn’t feasible for the customer, teams can leverage SAP Concur’s standard accounting extract and a middleware solution to integrate SAP Concur with their customer’s ERP solution.
SAP Concur integration with SAP S/4HANA consists of four key areas:
- SAP Concur connectivity: System prep, installation, and middleware (ICS or client specific)
- Master data integration: HR employee data, cost object data, and project staffing data
- Finance data integration: Expense posting data and cash advance posting data
- Credit card integration: Credit card feed and purchasing card feed
For customers that operate their HR and financials within SAP, ICS allows for the automatic replication of HR and cost object data between SAP Concur and SAP, and automation of expense postings in SAP from SAP Concur. This integration provides a more responsive system, allowing the business to change reports or invoices once they’ve been extracted.
Finance Integration with SAP Concur: Note the following points regarding finance integration with SAP Concur:
- ICS will require an SAP Concur test site in which the customer installs specific SAP Concur add-ons in SAP, as well as an SAP Concur technical resource to enable ICS for master data and financial accounting integration.
- The ICS setup will require a remote function call (RFC) connection to the SAP Concur host site and the appropriate SAP security access to enable ICS.
- Using ICS won’t require custom interface development to facilitate integration, and business add-ins (BAdIs) can be modified in order to alter the standard posting process.
SAP Fieldglass
SAP Fieldglass is a cloud-based vendor management system (VMS) acquired by SAP in 2014. It’s designed to help organizations procure external services and manage contingent workforce processes, from onboarding to invoicing. SAP offers robust, reliable, secure, and seamless integration of SAP Fieldglass with SAP S/4HANA.
SAP Fieldglass offers a host of extensive finance and HR functionality including but not limited to the following:
- Multibid statement of work (SOW)
- Onboarding
- Seamless integration with SAP S/4HANA
- External workforce management
- Timesheets
- Invoicing
Let’s discuss how SAP Fieldglass integrates into an existing SAP S/4HANA system. As shown in the figure below, the entire source-to-pay process for contractors is automated, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of overdue payment while simultaneously boosting productivity. As soon as the timesheet is approved in SAP Fieldglass, an invoice is generated against it, which in turn will create a service entry sheet in SAP S/4HANA, enabling cost distribution across the relevant cost centers. This eliminates the tedious work of manually processing invoices. There’s additional support for non-purchase order invoices as well.
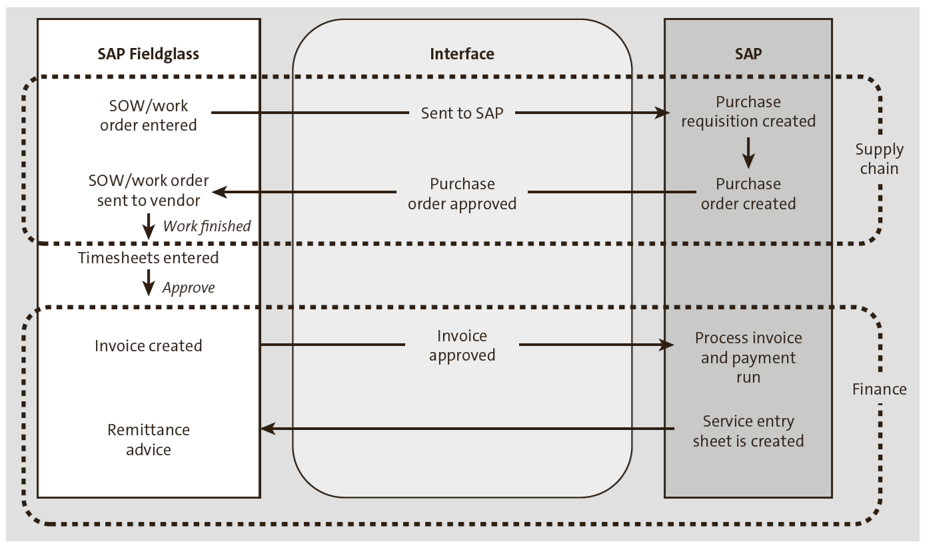
SAP Fieldglass Integration with SAP S/4HANA: SAP Fieldglass comes out of the box with many preconfigured standardized templates and configurations. These templates take minimal effort to use, requiring only basic setup. Included are standardized integration scenarios that provide predefined field mappings for master data for seamless integration with SAP S/4HANA, including finance master data (WBS elements, cost centers, etc.), as well as supply chain master data (vendor, material, etc.). SAP Fieldglass has built-in functionality through which it can be configured to mimic the financial and organizational configuration of SAP S/4HANA.
SAP SuccessFactors
SAP SuccessFactors is a cloud-based human capital management (HCM) solution acquired by SAP in 2012. The SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central module stores all master data relevant for employees, such as ID, name, contact information, photo, job description, position information, employment status, and so on. SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central has the added ability to store contingent worker information as well.
In addition to SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central, the following submodules can be enabled and configured in the SAP SuccessFactors HCM suite:
- SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting
- SAP SuccessFactors Onboarding
- SAP SuccessFactors Compensation
- SAP SuccessFactors Performance & Goals
- SAP SuccessFactors Succession & Development
- SAP SuccessFactors Learning
- SAP SuccessFactors Workforce Analytics
There are multiple methods of integrating information from the SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central module into SAP S/4HANA, based on the type of SAP SuccessFactors implementation:
HR Mini Master Replication
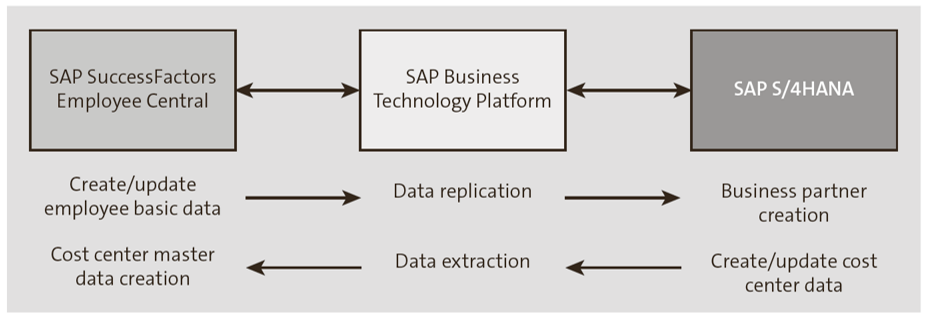
This integration option should be selected when SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central is the system of record for HR data, but HR processes, such as time management and payroll, are processed in SAP S/4HANA. This integration option replicates HR data from SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central to the SAP S/4HANA system to support time and payroll processing. Backwards integration from SAP S/4HANA to SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central is also required to ensure cost center master data is in sync, as shown here.
Without HR Mini Master Replication
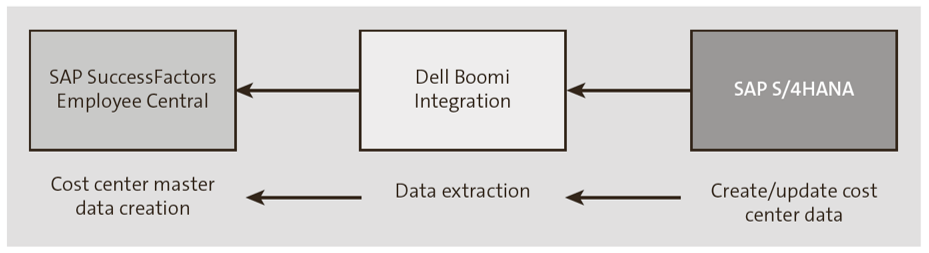
This integration option should be selected when HR processes aren’t run in an SAP S/4HANA system and SAP SuccessFactors manages them instead. This assumes that other financial or project-related business processes in SAP S/4HANA don’t require HR data. This integration option will ensure cost center master data is passed from SAP S/4HANA to SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central to ensure that the systems are in sync. Since HR data isn’t required in SAP S/4HANA, there’s a single direction for this integration from SAP S/4HANA to Employee Central via Dell Boomi as the middleware, as shown in the final figure.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book SAP S/4HANA Finance: An Introduction by Maunil Mehta, Usman Aijaz, Sam Parikh, and Sanjib Chattopadhyay.



Comments