A business partner represents the highest-level object in an SAP S/4HANA system.
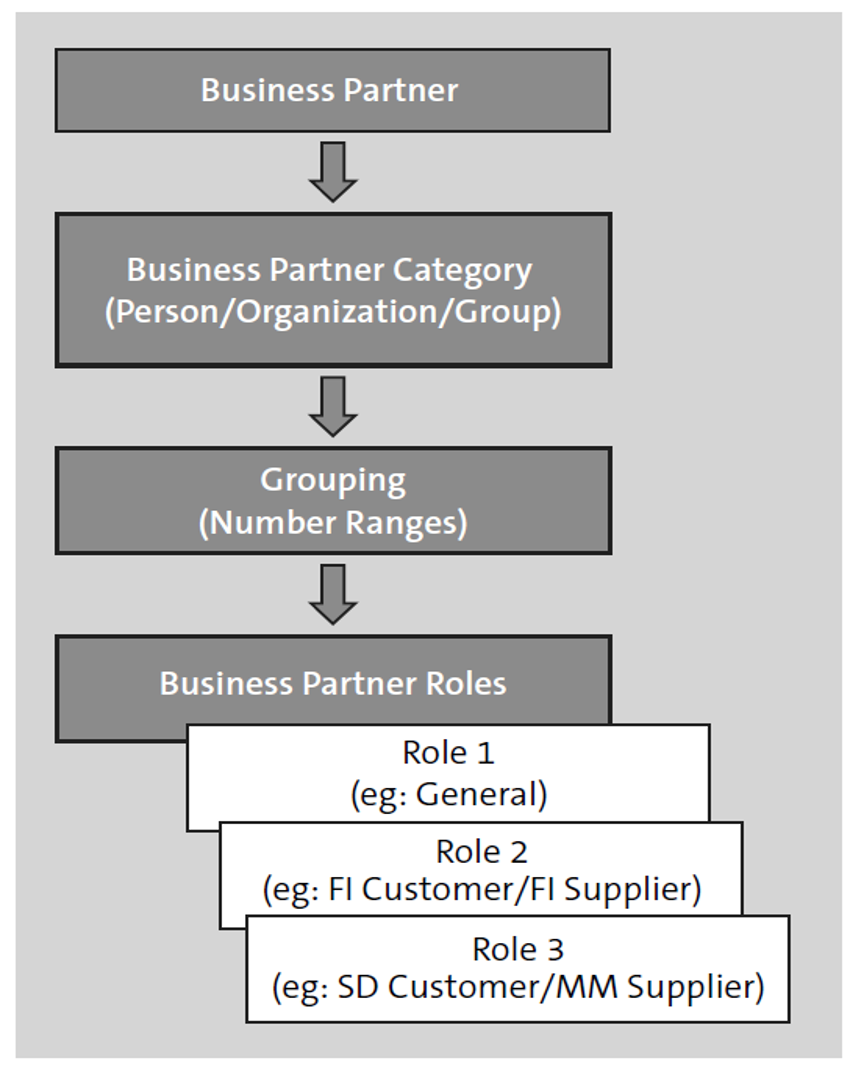
A business partner can be a person, an organization, or a group. A business partner can be characterized by the following basic structure:
- Business partner categories
- Grouping
- Business partner roles
Let’s now discuss the structure of a business partner in SAP S/4HANA.
Business Partner Category 1
As already mentioned, the business partner represents the highest-level object in the entire structure and consists of categories, such as person, organization, or group. The business partner category determines which data can be used for a particular business transaction. It’s used to define general attributes such as name and address. A business partner is always assigned to exactly one business partner category (person, organization, or group). This assignment can’t be changed in the future, nor can the predefined SAP business partner categories be extended. The following categories are available to be chosen:
- Person: Natural person, private person.
- Organization: Legal entity or part of a legal entity, for example, company, department in a company, club, or association.
- Group: For example, marriage or shared apartment.
When a user creates a business partner using Transaction BP, it’s mandatory to first select the business partner category. Based on the selected business partner category, the system will only then provide the relevant fields for master data entry.
After the business partner has been created using Transaction BP, it’s easier for a user to recognize the different business partner categories in the master record by the different symbols when processing them again. The person category is represented by a stylized icon , the organization category is represented by a factory icon, and the group category is represented by an icon showing two heads.
Note: If there’s no business need to select a business partner category at all, then it can be hidden using the SAP standard system via BAdl BUPA_PARTNER_CATEGORY.
If the category Person is chosen while creating a business partner, then some of the basic fields that appear are as follows:
- First Name
- Last Name
- Academic Title
- Address Overview
- Address Usage
- Birth Date
- Country
- Employer Status
- Identification
- Bank Data
If the category Organization is chosen while creating a business partner, then some of the basic fields that appear are as follows:
- Company Name
- Company Title
- Address Overview
- Address Usage
- Legal Form
- Identification
- Industry
- Tax Number
- Foundation Data
Business Partner Grouping
The business partner grouping reflects the logical and structured grouping that a company follows while dealing with its various internal and external stakeholders. The internal stakeholders are, for example, employees, while the external stakeholders can be customers and vendors. The business partner grouping defines the number range of the business partner. The account group defines the number range of the customer or vendor master record. Together, these two groups determine the numbers in which a business partner and a customer or a vendor are created.
Meanwhile, note the following for a business partner grouping:
- Similar to the SAP S/4HANA Finance account group for customers or for vendors
- Mandatory for each business partner
- Defined in Customizing
- Used to assign number ranges (internal/external) to business partners
Business Partner Role
A business partner role is used for the business classification of a business partner (see below). The characteristics and attributes within the business partner role result from the requirements that the respective business relationship places on the link between a business partner role and a company. The link can be characterized by several roles, and each of these different roles defines a very specific type of business relationship, such as customer, goods supplier, vendor, bill recipient, biller, and so on.
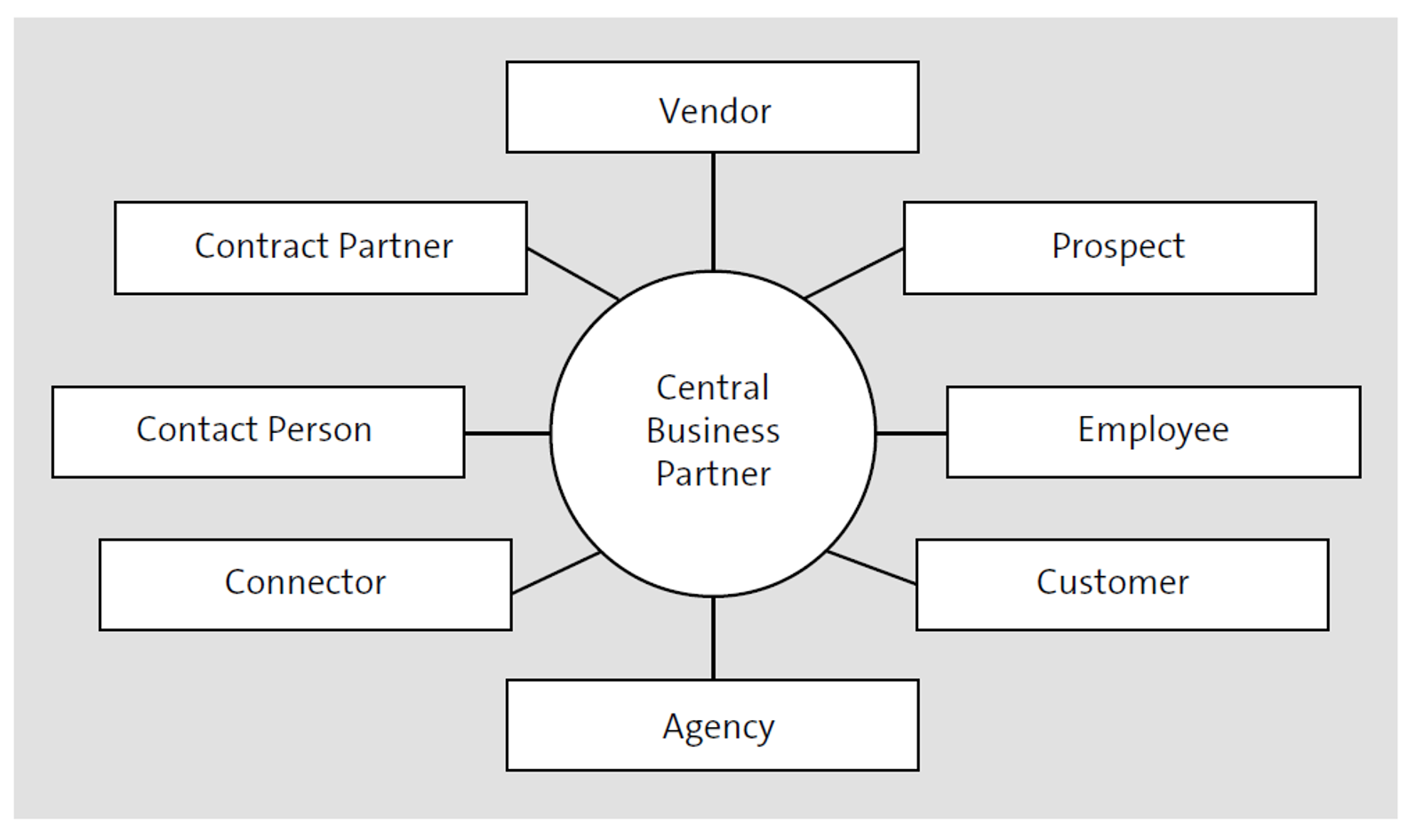
Let’s take a look at the process of processing a customer invoice, for example. Here, a company needs a role in which details of the payment terms can be stored, that is, FI customer. If the business partner is also a vendor, vendor-related data such as the delivery address will be required. This data will accordingly be maintained in the role MM vendor. If a business partner is both a customer (he buys goods from a company) and a vendor (he also delivers goods to a company), the customer master record will be stored in the role customer (SD), and the vendor master record in the role vendor (MM) for these business relationships. The link between the two roles (master records) is defined, as in SAP ERP, by entering the vendor number in the customer master record and the customer number in the vendor master record. A role can only be added and not removed, but the limited effectiveness can be achieved by using validity periods. Consider the following regarding business partner roles:
- Roles define the display and the data of a business partner.
- SAP S/4HANA provides predefined roles.
- Customer-specific roles can also be customized.
- The Business Data Toolset (BDT) is used to influence the GUI.
Note: The customization settings for the category Persons can be made via the menu path SAP IMG > Cross-Application Components > SAP Business Partner > Business Partner > Persons. Here, maintain entries for name components such as academic titles, name affixes and prefixes, and occupations. In addition, you can maintain entries on gender, marital status, and nationality that can then be used in the Identification tab of a business partner.
The customization settings for the category Organizations are made via the menu path SAP IMG > Cross-Application Components > SAP Business Partner > Business Partner > Organizations. Here, maintain entries for industry systems, industries, and the legal framework. The entries maintained here can then be used while creating a business partner of category Organization.
The settings for the category Groups are made via the menu path SAP IMG > Cross- Application Components > SAP Business Partner > Business Partner > Groups. Different group types can be defined here that can then be used while creating a business partner of category Group.
Learn more about how SAP S/4HANA simplifies the business partner functionality in this post.
Editor’s note: This post has been adapted from a section of the book Business Partners in SAP S/4HANA: The Comprehensive Guide to Customer-Vendor Integration by Jawad Akhtar. Jawad is an SAP logistics and supply chain management expert with a focus on business sales and delivery. He earned his chemical engineering degree from the Missouri University of Science and Technology in the United States. He has more than 20 years of professional experience, 16 of which have been spent working with SAP systems. He has experience working on several large-scale, end-to-end SAP implementation project lifecycles, including rollouts. He works with SAP clients to help them identify the root causes of business issues and address those issues with the appropriate SAP products and change management strategies. He now focuses on next-generation SAP products such as SAP S/4HANA, SAP Integrated Business Planning, SAP Ariba, and SAP Customer Experience.
This post was originally published 8/2022.



Comments